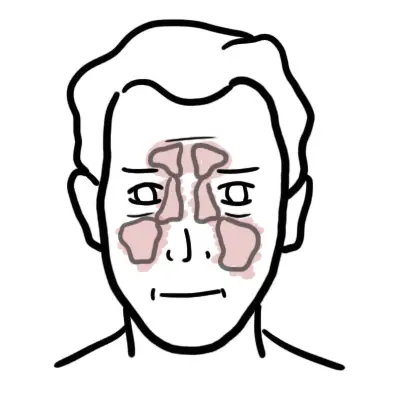
Overview Rhinosinusitis is one of the more prevalent chronic illnesses worldwide, affecting individuals of all ages. It is an inflammatory process that involves the nose and paranasal sinuses. Rhinosinusitis may be acute or chronic. Chronic rhinosinusitis can be subject to acute exacerbations.
| Definition Rhinitis: Irritation and inflammation of the mucosa lining the nasal cavity Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses (usually a result of rhinitis) Acute rhinosinusitis: Acute inflammatory condition of the nose and paranasal sinuses |
| Kartagener's Syndrome also known as primary ciliary dyskinesia is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes defects in the action of cilia lining the respiratory tract |
Clinical Presentation - Acute rhinosinusitis
Clinical Presentation - Chronic rhinosinusitis
Clinical Examination
Acute rhinosinusitis
Chronic rhinosinusitis
Stasis of secretion results in cessation of bacterial export, propagating mucosal inflammation and compromising aeration of the mucosa. This in turn leads to increased ciliary dysfunction and the vicious cycle continues, resulting in CRS.
Acute rhinosinusitis
Chronic rhinosinusitis
Complications
Frontal sinusitis
Ethmoid sinusitis
Maxillary sinusitis
Sphenoid sinusitis
Prognosis Acute rhinosinusitis is very common and most cases resolve without any long-term sequelae.
