Price range: $3.95 through $24.95
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive lung disease that is characterized by the formation of scar tissue (fibrosis) in the lungs. It is a type of interstitial lung disease, which means that it affects the tissue and structures between the air spaces of the lungs.
IPF is a rare condition that usually affects people over the age of 50, and it is more common in men than in women. The exact cause of IPF is not fully understood, and it is classified as “idiopathic,” meaning that the cause is unknown. However, it is believed to be related to an abnormal immune response or an inherited genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of IPF may include shortness of breath, a dry cough, fatigue, and weight loss. The disease typically progresses slowly over time, and it can be difficult to diagnose early on, as the symptoms may be similar to those of other respiratory conditions.
Diagnosis of IPF typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and lung function tests. There is no cure for IPF, and treatment is focused on slowing the progression of the disease and managing symptoms. This may include medications to reduce inflammation and scarring, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking.
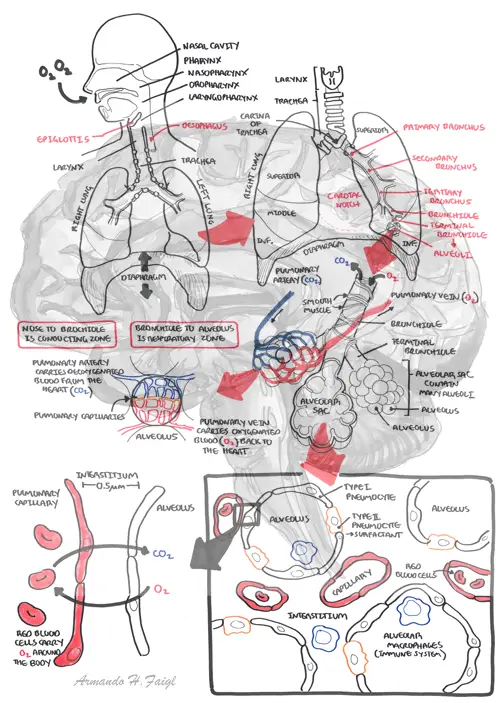
It's an educational diagram concisely outlining the specific concept. Armando Hasudungan's diagrams are popular learning aids, allowing the reader to quickly and easily comprehend a complex topic. It's a valuable tool in teaching, self study, and presentations.
The content is subject to copyright and your purchase allows permission for different types of use.
Personal use:
Commercial use:
Put simply, you are not the intended user and you are providing the content to users in exchange for money then it is considered commercial and you must purchase the commercial licence.
All usage licences are considered lifetime licences.
Refunds are no table to be granted once the file has been downloaded because the content is delivered as a downloadable file. For issues with the file download please reach out to us and we'll gladly assist you.
All our diagrams are delivered as high quality PDFs.
Yes! All the infographic PDFs are printer friendly. Please note that some of them are poster size and are best printed on A3/poster paper, however you are able to simply 'tile' larger images (spilt them across multiple A4/letter pages) and then stick them together.

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.