Description
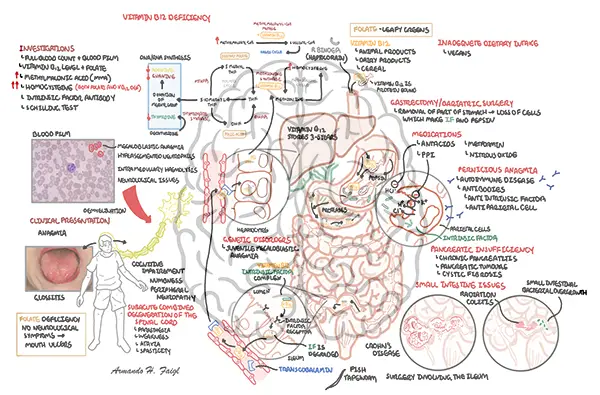
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a condition that occurs when the body does not have enough vitamin B12, a nutrient that is essential for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system, as well as the production of red blood cells.
There are several mechanisms by which vitamin B12 deficiency can occur:
- Insufficient intake: Vitamin B12 is found mainly in animal-derived foods such as meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Individuals who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet may be at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency if they do not consume enough fortified foods or supplements.
- Absorption issues: Vitamin B12 is absorbed in the small intestine, and the absorption process requires the presence of a protein called intrinsic factor. If intrinsic factor is not present or if the small intestine is damaged, vitamin B12 absorption may be impaired. This can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and metformin, can interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12.
- Age-related factors: As we age, the production of intrinsic factor may decline, leading to impaired vitamin B12 absorption.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and gastrointestinal disorders, can also contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency.
Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency may include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and tingling in the hands and feet. It is important to diagnose and treat vitamin B12 deficiency promptly, as it can lead to serious complications if left untreated.

