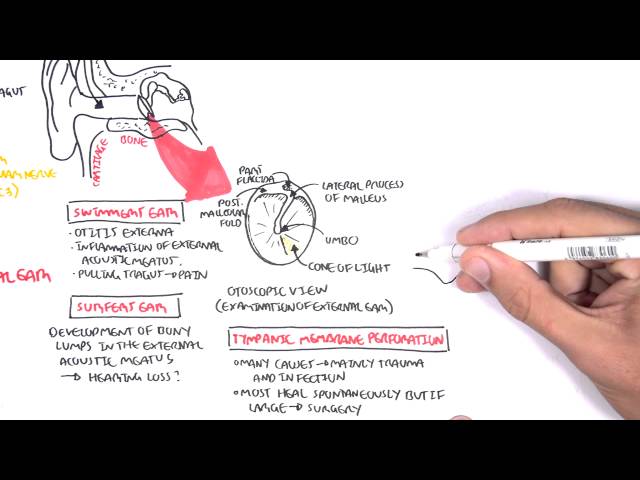
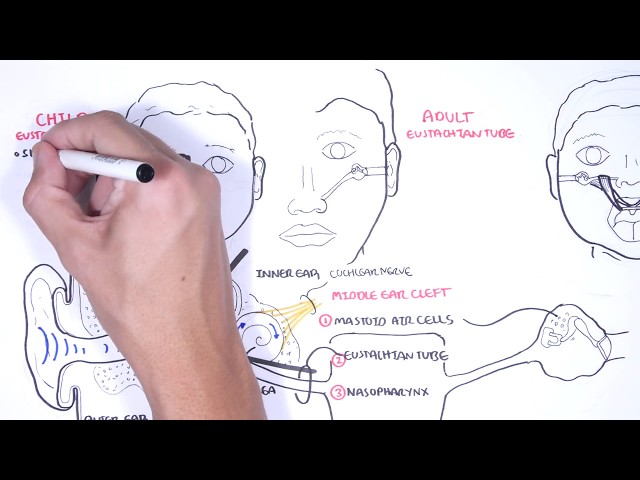
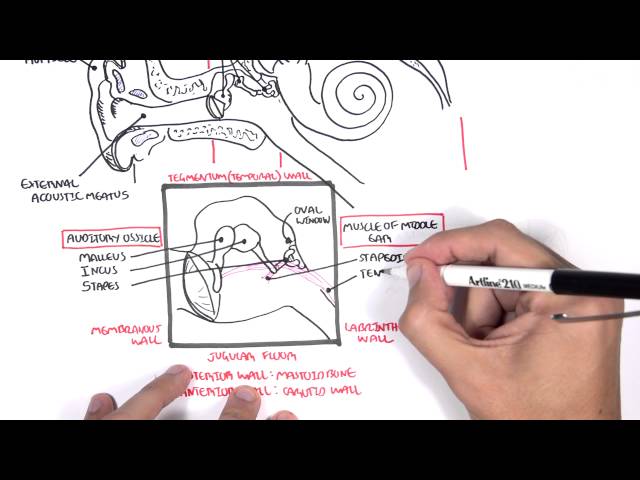
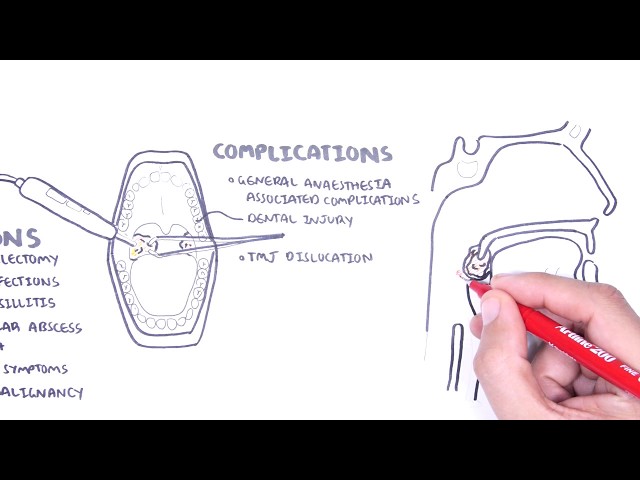
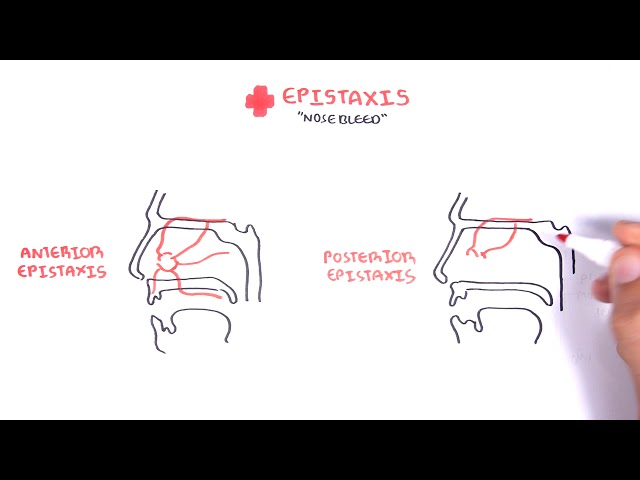
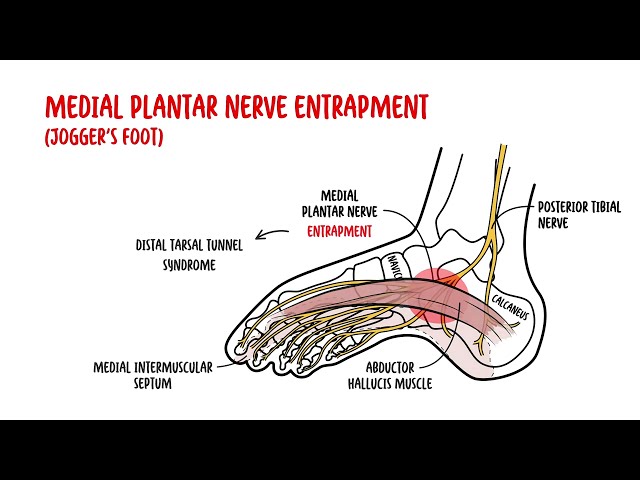
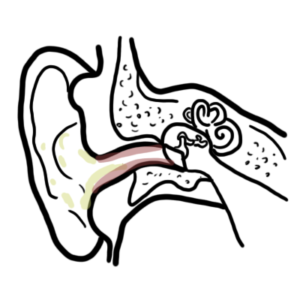
0:00 Hello, in this video, we're going to talk about autalgia. 0:10 Autalgia comes in a Greek word "ot" which means "ear" and "algas" which means " 0:14 pain", 0:14 so literally means "painful ear". 0:17 The ear is a structure that can be divided into three parts, the inner, middle, 0:21 and external 0:22 ear. 0:23 Autalgia usually describes the painful ear caused by pathology in the external 0:28 and middle 0:29 ear. 0:30 There are so many sensory nerves which innervate the areas of the external ear 0:34 to the middle 0:35 ear. 0:36 Many of these nerves also innervate other organs in our body. 0:40 Because of this, pain in the ear may not be due to pathology in the ear but 0:44 rather referred 0:45 pain from inflammation elsewhere in the body. 0:50 Our body have 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves, 8 pairs 0:57 of which 0:58 are actually cervical, abbreviated C. 1:03 The trigeminal nerve which is cranial nerve number 5 have three main branches 1:07 and its 1:08 role is for sensation of the face in a specific distribution depicted in this 1:14 diagram. 1:14 You have trigeminal branch 1, trigeminal branch 2, trigeminal branch 3, abbrevi 1:21 ated V1, V2, 1:23 V3. 1:24 The third branch of the trigeminal nerve V3 is the mandibular nerve and it inn 1:28 ervates part 1:29 of the external ear. 1:32 This means it also innervates the oracle and external acoustic meatus, the ear 1:43 canal. 1:44 Which is the cervical spinal nerve 2 and cervical spinal nerve 3 innervates the 1:48 other 1:49 major portion of the external ear. 1:53 So far the external ear is supplied by cranial nerve number 5, branch 3 and 1:59 then also the 1:59 branches of cervical nerves 2 and cervical spinal nerve 3. 2:05 Another nerve that also supplies the external ear is the facial nerve. 2:08 Now the facial nerve is cranial nerve number 7. 2:13 It has important sensory role in special taste sensation to the anterior 2/3 of 2:18 the tongue. 2:19 The facial nerve travels through what is called the facial canal which actually 2:24 is in close 2:25 proximity to the middle ear. 2:28 Branches of the facial nerve also innervates part of the external ear and 2:33 supplies the 2:34 middle ear structures, some of them. 2:40 The glossopharyngeal nerve, cranial nerve number 9 innervates the oropharynx, 2:45 the carotid 2:46 bodies and sinus, the posterior 1/3 of the tongue as well. 2:51 But it also innervates the middle ear cavity and the eustachian tube. 2:59 The vagus nerve which is cranial nerve number 10 is an important nerve known 3:03 for its parasympathetic 3:05 function. 3:06 It innervates many organs in our body including the heart, the lungs that are 3:10 just in track, 3:11 it also innervates the middle ear, the external acoustic mutis and part of the 3:18 oracle. 3:19 Cleaning the ear with earbuds can stimulate the vagus nerve, this is the reason 3:24 why when 3:24 people clean their ears they also cough because the vagal nerve reflex. 3:30 In summary, the oracle is affected or innervated by cranial nerve number 5, 7, 3:37 cervical spine 3:38 nerve 2, C3, the external auditory meadeus and canal bacranial nerves 5, 7 and 3:46 10 and 3:48 the middle ear including the tympanic membranes by cranial nerve 10 and 9. 3:54 Irritation of any portion of these nerves can result in autalgia. 3:59 A good way to categorize autalgia which is ear pain is into primary autalgia 4:04 and secondary 4:05 autalgia. 4:07 Pain that originates from the ear is called primary autalgia and the most 4:11 common causes 4:12 are otitis media and otitis external which again is more common in children. 4:18 Secondary autalgia is referred pain and is more common in adults. 4:25 Temples of primary autalgia include acute autitis media which is an infection 4:29 of the middle ear 4:30 caused by bacteria and usually preceded by a viral infection. 4:35 Pain is felt deep within the ear and children complain of nonspecific symptoms 4:40 such as irritability, 4:42 poor sleep and feeding. 4:45 Autitis external also known as swimmer's ear is infection of the external ear 4:49 typically 4:50 by bacteria pseudomonas originosa and staphylococcus aureus. 4:54 Autitis external is characterized by pain and tenderness localized to the 4:58 external ear canal. 5:01 Malignant autitis external as the name suggests doesn't mean malignancy like 5:06 cancer rather 5:07 malignant autitis external is where autitis external actually spreads the 5:12 infection spreads 5:13 to surrounding bones of the skull, base and this will produce an intense pain 5:19 and obviously 5:20 signs of toxicity and fever. 5:24 Another cause of primary autalgia is eustachian tube dysfunction due to viral 5:28 infection for 5:29 example and this will cause swelling of the eustachian tube and thus ear pain. 5:35 Foreign body may present with pain and discomfort or even hearing loss as the 5:40 first presentation. 5:42 Euryngitis is a painful condition that may be caused by a viral infection of 5:47 the tympanic 5:48 membrane. 5:52 Cholestiotoma is a rare but serious complication of autitis media with effusion 5:59 . 5:59 Cholestiotoma is where a benign mass of epithelial tissue develops in or behind 6:04 the tympanic 6:05 membrane and can erode into the bone of the ear canal. 6:10 Another cause of a painful ear is to cellulitis of the oracle which is 6:17 basically the cut your 6:18 ear itself and this will develop usually after trauma or an insect bite or even 6:24 ear piercing. 6:27 Herpes zoster infection which is shingles is essentially reactivation of the 6:31 chicken 6:32 pox virus and this can manifest in the outer ear. 6:38 If it's associated with facial weakness this is termed ramzi hunt syndrome and 6:43 this is 6:44 due to facial nerve involvement because remember the facial nerve runs very 6:50 close to the middle 6:52 ear. 6:53 Now, ramzi hunt syndrome is rare in children as herpes zoster shingles tend to 6:59 manifest 6:59 later in life. 7:02 Mass stoiditis is a complication of acute otitis media and it's essentially 7:06 infection 7:07 of the mastoid air cells. 7:10 The infection can actually spread to the mastoid air cells through the mastoid 7:15 antrum. 7:16 Typically it presents with fevers, post-arricular erythema and tenderness. 7:22 Mastoiditis is a serious infection because the infection from the mastoid air 7:27 cells can 7:28 then further spread into the brain, the meninges and even down to the neck. 7:34 So those are some examples of primary otolgia which is really ear pain caused 7:39 by pathology 7:40 in the actual ear. 7:42 Secondary otolgia is caused by referred pain from shared nerves of the ear. 7:48 Secondary otolgia can usually be identified by the absence of findings in the 7:53 ear itself 7:54 and by findings of inflammation elsewhere. 7:58 For example, referred otolgia may originate from the temporal mandibule joint, 8:03 the teeth, 8:04 the pharynx and even the larynx.