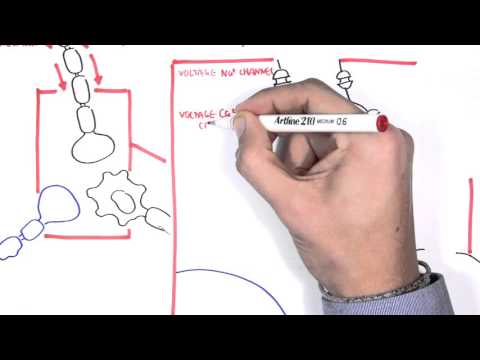
0:00 Hello, in this video we're going to talk about another disease modifying anti- 0:09 romatic 0:10 drug by the name of sulfasalazine. 0:14 Sulfasalazine is an immunomodulator used to treat inflammatory bowel disease, r 0:19 heumatic 0:20 arthritis, psoriarcharitis, and peripheral spondyloethropathies. 0:27 Sulfasalazine is probably more well known for its use in inflammatory bowel 0:31 disease. 0:32 There are two types of inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, which 0:35 involves 0:36 superficial inflammation of the rectal zigmoid area, and progresses proximally, 0:43 and then 0:43 there's Crohn's disease, which is a transmural inflammation involving the ili 0:48 osecal region, 0:50 and can really affect anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract in patches. 0:59 Sulfasalazine is a prodrug, composed of 5 amino salicylic acid linked to sulfur 1:05 peridine 1:06 through an azobon. 1:09 The linkage minimizes absorption of the drug in the upper gastrointestinal 1:20 tract. 1:21 In the colon, however, bacteria break the azobon and free both sulfur peridine 1:28 and 1:29 5 amino salicylic acid. 1:35 They break the azobon and free both sulfur peridine and 5 amino salicylic acid. 1:45 In inflammatory bowel disease and other rheumatological conditions, a retinoid 1:51 acid formed from 1:52 cell membranes of cells is converted to prostaglandins and leukotrines via 2:00 enzymes, cyclooxygenase 2:03 and lipooxynese. 2:06 Prostaglandin and leukotrines essentially promote inflammation. 2:11 Inflammation in a particular tissue stimulates cells and their transcription 2:17 factor, including 2:18 nuclear factor kappa B. 2:21 When activated, it essentially promotes the production of proinflammatory cytok 2:28 ines, including 2:29 tineph alpha and interleukin 1. 2:31 All these cytokines and peptides creates an inflammatory environment, 2:35 attracting more 2:36 immune cells such as neutrophils to the area. 2:41 5 amino salicylic acid, or 5 ASA, acts locally as an anti-inflammatory molecule 2:50 by inhibiting 2:51 enzymes, cyclooxygenase and lipooxygenase locally, as well as nuclear factor k 2:57 appa B. 2:59 Thus, sulfacylazine reduces inflammation. 3:07 The other half of sulfacylazine sulfur peridine is absorbed, metabolized in the 3:15 liver and 3:16 eventually excreted in urine. 3:19 For peridine is responsible for exerting the systemic actions, the adverse 3:24 effects of sulfacylazine. 3:26 Serious side effects to remember, aside from nausea and vomiting, include blood 3:31 , dyscrazia, 3:33 hepatitis and hypersensitivity reactions. 3:37 People who have sulfur allergies are more prone to side effects. 3:41 Finally, an important side effect is the risk of low sperm count in males. 3:48 I hope you enjoyed this video on sulfacylazine, which is an immunomodulator 3:52 used to treat 3:53 many rheumatological conditions, mainly well known for treatment in 3:57 inflammatory bowel disease.