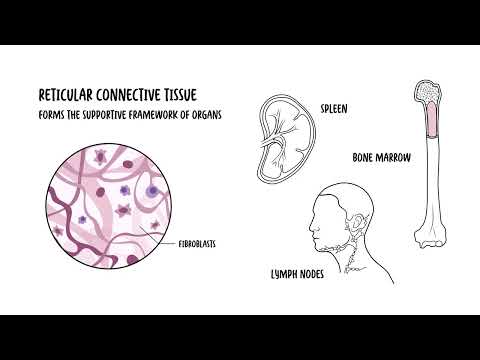
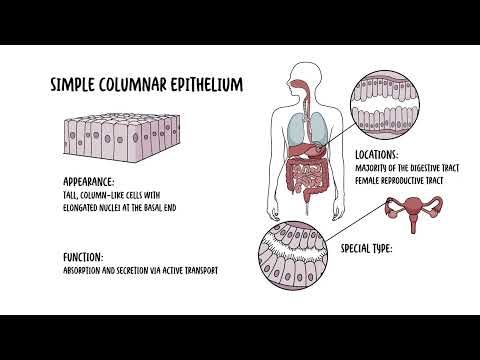
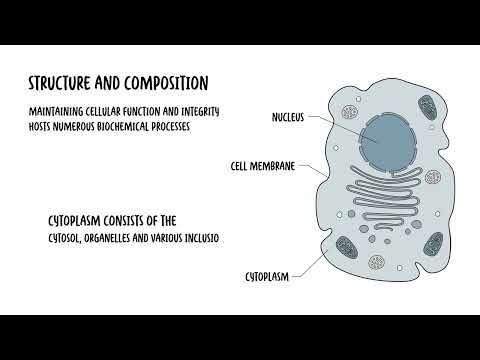
0:00 Hello, in this video, we're going to talk about tissues. 0:11 A tissue is a group of similar cells and cell products that work together to 0:15 perform a specific 0:16 structural and physiological role in an organ. 0:20 These tissues are organized into various types, each with distinct structures 0:23 and function. 0:25 Although there are many types of cells in our body, they are organized into 0:29 four broad 0:30 categories of tissues. 0:31 These are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, nervous tissue, and muscular 0:37 tissue. 0:38 The tissues differ to each other by the type and function of the cells that 0:42 make up the 0:42 tissues. 0:43 The tissues also differ by the characteristic of the matrix, which is really 0:47 the substance 0:48 that surrounds the cells and the amount of space occupied by the matrix versus 0:54 the cell, 0:55 so the ratio essentially. 0:58 Let's take a look at the features of the four primary types of tissues, 1:01 beginning with epithelial 1:03 tissue. 1:10 Epithelial tissue, for example, is composed of layers of closely spaced cells. 1:16 So, epithelial tissues are composed of cells that are packed tightly together. 1:21 You can think of them as bricks on the wall. 1:24 They contain minimal matrix. 1:27 Epithelial tissues cover the body surfaces, so they actually make up your skin. 1:32 They cover external and internal lining of organs. 1:36 And because of this, they serve many roles. 1:40 They serve for protection, secretion, excretion, filtration, and absorption, 1:47 particularly in 1:48 glands and the kidneys, for example, where they are found abundantly. 1:59 Nervous tissue is a second type of tissue, which consists of neurons and 2:03 supporting cells 2:04 called glial cells in high numbers. 2:08 Nerv cells really transmit signals and information to other cells. 2:13 They serve as communicators, essentially, throughout our body. 2:23 Muscular tissue are composed of elongated, excitable cells that are specialized 2:29 for contraction 2:31 and movement. 2:32 They are not only responsible for movement, muscle is also dependent for the 2:37 process of 2:37 digestion, moving food down your gastrointestinal tract, waste elimination, 2:42 breathing, muscles 2:43 to help you breathe, speech, and blood circulation. 2:52 There are actually three types of muscle tissue. 2:55 There are skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. 2:59 Sclilo muscle is voluntary. 3:01 There are muscles that help movement, such as bending my arm. 3:06 Chronic and smooth muscles are involuntary. 3:09 Cardic muscles contract to pump blood out of the heart, and smooth muscles line 3:13 up the 3:14 blood vessels and our intestines to help move things down the pipe. 3:25 Lastly is connective tissue. 3:28 Connective tissue is much more complicated, I think. 3:31 Connective tissue is a tissue that really connects or separates and supports 3:34 all other 3:35 types of tissues in our body. 3:37 Like all other tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment 3:43 of fluid, 3:43 the matrix. 3:44 But, in this case, we'd like to call it the extra cellular matrix, because they 3:49 're outside 3:50 the cell, remember. 3:51 However, connective tissue differs from other types of tissue in that the cells 3:57 are loosely 3:58 rather than tightly packed within the extra cellular matrix. 4:06 Based on the cells present and the extra cellular matrix structure, we differ 4:13 two types 4:14 of connective tissue. 4:16 You can have connective tissue proper and specialized connective tissue. 4:20 Now, there are many other types or ways that connective tissue can be 4:23 categorized, but 4:25 I think this is an easy way. 4:27 So connective tissue proper can be further divided into loose connective tissue 4:31 and dense 4:31 connective tissue. 4:33 Disc connective tissue include blood, bone, and cartilage. 4:44 The next level of organization after tissue are your organs, where several 4:49 types of tissue 4:50 come together to form a working unit. 4:53 Two or more tissue types make up an organ, such as your spleen, your skin, and 4:58 your heart. 5:04 So, in summary, we have four types of tissues in our body – epithelial tissue 5:09 , connective 5:11 tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. 5:15 We will delve into each type of tissues in separate videos. 5:18 Thank you. 5:33 [BLANK_AUDIO]