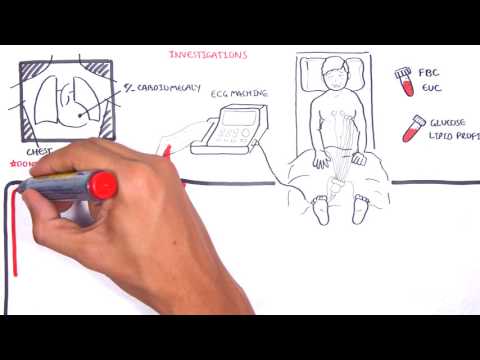
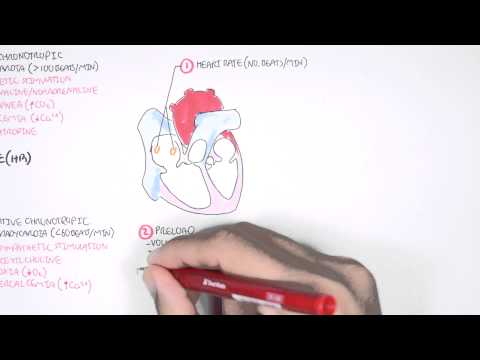
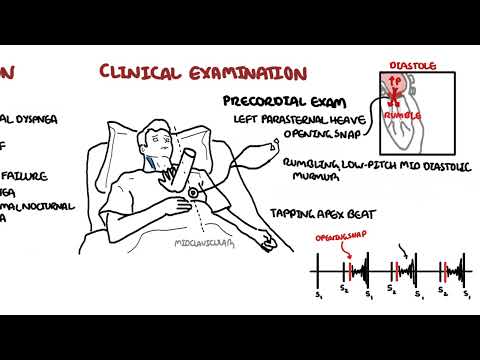
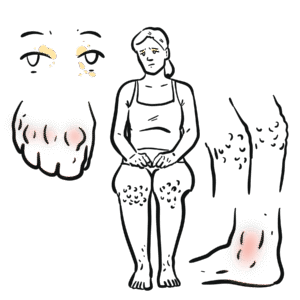0:00 Heart failure is a disorder in which the heart cannot pump blood to the body at 0:08 a rate that 0:09 is needed, causing symptoms of shortness of breath and fatigue. 0:13 To better understand heart failure, we need to review the heart's function. 0:17 The heart has two phases during each heartbeat, filling, which is diastole, and 0:22 pumping, which 0:22 is systole. 0:25 The heart function of the heart and resulting cardiac output is governed by 0:29 four major determinants. 0:32 These are the contractility of the myocardium, the actual muscle of the heart, 0:36 the preload 0:37 of the ventricles, the amount of blood filling the ventricles prior to systole. 0:43 The afterload applied to the ventricles, essentially what the ventricles have 0:48 to overcome 0:49 to push blood out of the heart and the heart rate. 0:54 The cardiac output equation can be simplified nicely to stroke volume, which is 1:00 the amount 1:00 of blood the ventricles pump out during each heartbeat, multiplied by a heart 1:05 rate, which 1:06 will give you the cardiac output, where contractility, afterload and preload 1:11 all affect stroke volume. 1:15 Low cardiac output is a main feature in heart failure. 1:18 The heart fails to pump blood to the rest of the body. 1:22 When cardiac output is reduced, when the heart fails, a number of adaptations 1:27 occur, both 1:28 in the heart and systemically, and these are early adaptations and chronic 1:34 adaptations. 1:36 So in the early phases, when stroke volume is reduced, the amount of blood the 1:42 ventricles 1:43 pump with each heartbeat, this will actually increase the amount of blood left 1:48 in the ventricles 1:50 in diastole, and this is termed endistolic volume. 1:56 Because of this, the ventricular chambers fills with more blood. 2:00 The muscle fibers lengthen and tighten more, promoting a more forceful 2:05 contraction to eject 2:06 excess blood to compensate. 2:09 And this is the stalling law of the heart, as depicted in this graph. 2:14 The higher the endistolic volume, the stronger the force of contraction of the 2:18 ventricles 2:19 and so increasing stroke volume and cardiac output. 2:26 Reduced cardiac output is also picked up by the baroreceptors, which detect 2:31 this, and 2:31 will activate the sympathetic nervous system. 2:35 Sympathetic nervous system will stimulate myocardial contractility, increase 2:39 heart rate, 2:40 and venous tone to increase cardiac output. 2:44 Although these adaptations are designed to increase cardiac output, they may 2:48 themselves 2:48 be troublesome. 2:51 Sympathetic activation, long term, contributes to adverse ventricular remod 2:55 eling and progressive 2:56 ventricular dysfunction. 3:03 So in the chronic phases, with reduced cardiac output, what you also see is 3:08 reduced renal 3:08 blood flow, which will activate the renin angiotensin-eldosterone system. 3:16 The activation of the RAS system, essentially all of this will contribute to 3:20 ventricular 3:20 muscle remodeling and dysfunction. 3:28 With these chronic adaptations, there is eventual increase in pressures in the 3:31 ventricles themselves, 3:33 which then transmits this pressure to the atria, increasing atrial pressure, 3:38 and as a result, 3:39 this can lead to pulmonary congestion, and then even peripheral tissue 3:47 congestion. 3:49 And so this brings us to the clinical manifestation of heart failure, which is 3:53 easily classified 3:54 into right-sided heart failure symptoms and left-sided heart failure symptoms. 4:02 Left heart failure essentially causes a low cardiac output and can lead to 4:07 pulmonary congestion. 4:10 Low cardiac output symptoms and signs include presynthropy, fatigue and letharg 4:17 y, exertional 4:18 dysnia with orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dysnia, pulmonary congestion or ed 4:24 ema causes 4:25 shortness of breath, a chronic non-productive cough, coarse crackles at the 4:31 base, and 4:32 hypoxia. 4:35 Right side heart failure leads to congestion of peripheral tissue, which 4:40 manifests as a 4:41 raised jugular venous pressure, liver congestion, and pitting lower limb edema. 4:52 Ventricular muscle remodeling and hypertrophy and the subsequent dysfunction is 4:57 characteristic 4:57 of heart failure, and there are two broad remodeling processes that occur in 5:01 heart failure. 5:02 These are eccentric remodeling or concentric remodeling. 5:08 This also typically results in the pathological classification of heart failure 5:12 , with eccentric 5:13 remodeling typically causing heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and 5:18 concentric 5:19 remodeling typically causing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. 5:25 Projection fraction is the percentage of blood volume ejected by the heart with 5:31 each beat. 5:32 So a heart failure with reduced ejection fraction is less than 40%. 5:39 Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is greater than 50% of blood 5:44 ejected by the 5:44 heart with each heartbeat. 5:47 So heart failure with reduced ejection fractions, previously known as systolic 5:51 heart failure, 5:53 because there's a problem with pumping, the ejection fraction is low, less than 5:58 40%. 5:58 Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is previously known as diastolic 6:03 heart failure, 6:04 because there's an issue with heart filling, there's not enough space. 6:08 The distinction is important because the treatment of these two groups are 6:11 different. 6:12 Patients with ejection fraction of 41 to 95% are classified as "heart failure 6:17 with preserved 6:18 ejection fraction," borderline, and so they're usually treated the same. 6:27 Investigations to order with patients with heart failure typically include 6:31 brain-naturitic 6:32 peptide, which is a substance released by the ventricle, myocytes, in response 6:37 to ventricular 6:38 distension. 6:39 It is important to check full blood count electrolyte urea creatinine, an ECG 6:44 to look 6:44 for an underlying arrhythmia or a recent ischemic event. 6:50 Imaging studies include an echocardiogram, specifically looking at the ejection 6:55 fraction, 6:56 left ventricular size, as well as valvular pathology. 7:01 A chest x-ray typically shows cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion or edema, and 7:06 plural fusion. 7:09 Other investigations that can be ordered include stress imaging, left-heart cat 7:14 heterization 7:15 or right-heart catheterization. 7:18 Treatment of heart failure can be divided into non-pharmacological and pharmac 7:21 ological 7:21 management. 7:23 Non-pharmacological management is typically shared between the two and can 7:27 include fluid 7:27 restriction, reduced salt intake, stop smoking, stop alcohol drinking, exercise 7:34 , as well as 7:35 cardiac rehabilitation. 7:39 Pharmacological treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction 7:42 include asinhibitors 7:43 or angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers, spironolactone, fruzamide for 7:49 symptom management 7:50 or fluid overload, intresto, which is a combination of sacubitril and valsatin, 7:56 evabridine, as 7:58 well as SGLT2 inhibitors such as depactyl flowsin. 8:04 Pharmacological treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is 8:07 slightly different, 8:08 and this includes asinhibitors for hypertension, spironolactone, fruzamide for 8:14 management 8:14 of fluid overload, as well as SGLT2 inhibitors. 8:21 Surgical treatment is important, and this is mainly for heart failure with 8:24 reduced ejection 8:25 fraction. 8:26 And this includes cardiac re-synchronization therapy, implantable cardioverter 8:32 defibrillator, 8:35 ventricular assisted devices, as well as heart or cardiac transplantation. 8:41 So in summary, we've discussed heart failure, which can be broadly divided into 8:46 heart failure 8:46 with reduced ejection fraction and heart failure with preserved ejection 8:50 fraction. 8:51 And it's important to delineate between the two as treatment differs. 8:55 Thank you.