Spondylarthropathy
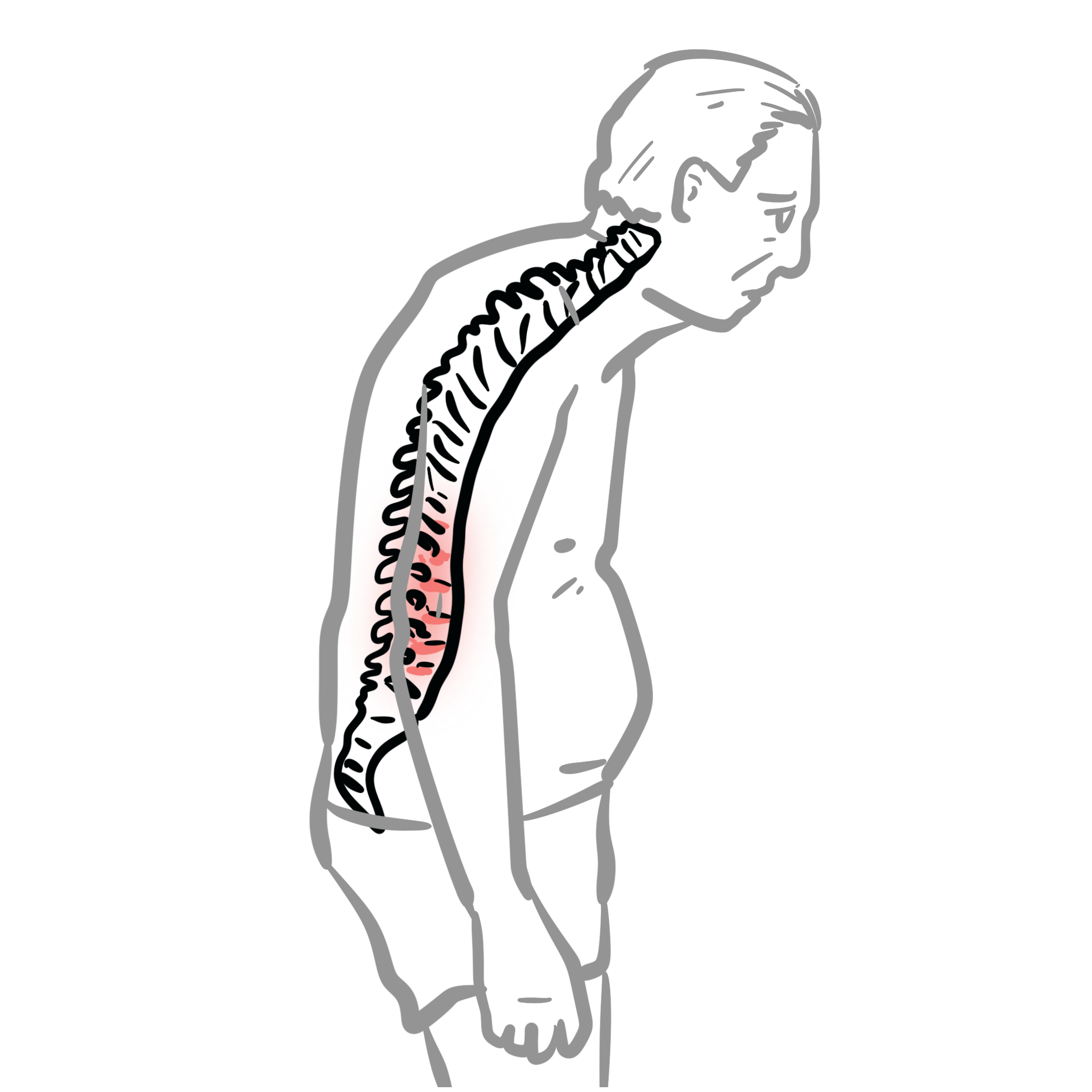

The spondyloarthropathies are a diverse group of inflammatory arthritides that share certain genetic predisposing factors and clinical features. Their most characteristic feature is inflammatory back pain. Enthesitis, another characteristic feature, involves inflammation at sites where tendons, ligaments, or joint capsules attach to bone.
Features of Spondylarthropathy
These diseases may also be accompanied by:
Main Spondylarthropathies
The HLA B27 molecule has an association with the spondyloarthropathies ranging between 50 and 95%. Interpretation of a positive result is complicated by the presence of this allele of the HLA B gene in up to 5–10% of the normal population.
| Type | Definition | Clinical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) | Chronic inflammatory disease primarily affecting the axial skeleton (spine, sacroiliac joints) | Inflammatory back pain, morning stiffness, reduced spinal mobility, uveitis, HLA-B27 positive |
| Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) | Inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis | Asymmetric peripheral arthritis, dactylitis, nail pitting, enthesitis, skin plaques |
| Reactive Arthritis (ReA) | Sterile arthritis triggered by infection (commonly GI or GU) | Triad: arthritis, conjunctivitis, urethritis; enthesitis, keratoderma, dactylitis |
| Enteropathic Arthritis | Arthritis associated with inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis) | Axial or peripheral arthritis, IBD symptoms, erythema nodosum, uveitis |
| Undifferentiated SpA | Features of SpA present but not meeting criteria for a specific subtype | Variable presentation — may have back pain, enthesitis, dactylitis, uveitis without clear subtype |

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion