Varicose Veins
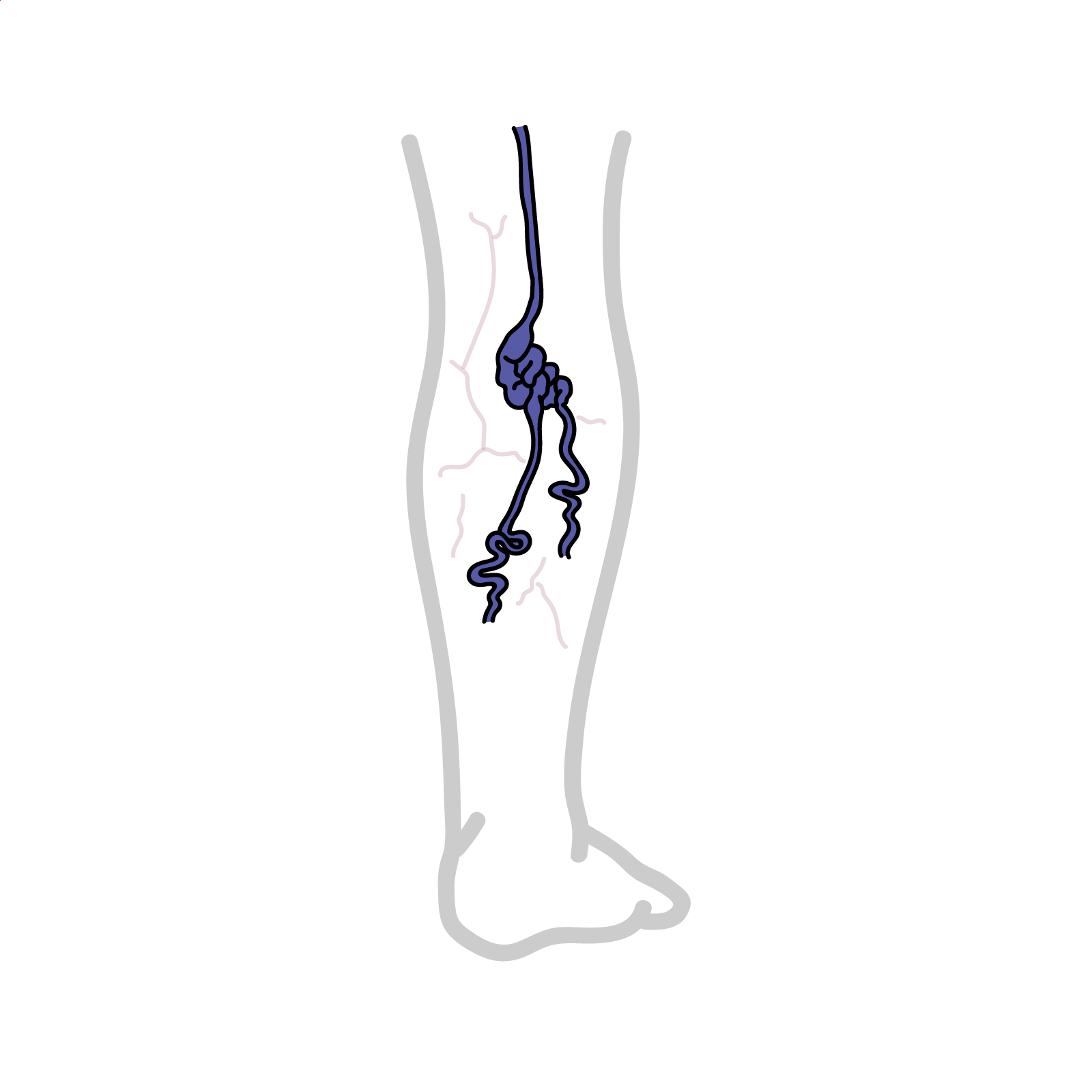

Varivose veins (VV) are long, torturous and dilated don’t veins of the superficial venous system. There is a spectrum ranging from telangiectasias (dilated interdermal venules less than 1 mm), through to reticular veins (non-palpable subdermal veins 1–3 mm) to varicose veins (greater than 3 mm). 35% of the general population affected.
The venous system of the leg can be divided into three groups:
Blood flows from the superficial system to the deep system via the perforator veins in the calf, and also at the Saphenofemoral junction, saphenopopliteal junction and mid-thigh perforators which contain one-way valves.
Primary
Secondary
| Risk Factors |
| Prolonged standing |
| Obesity |
| Pregnancy |
| Personal history |
| Family history |
| Contraceptive pill |
| Smoking |
Pathology
Clinical Presentation Patients complain about legs looking ugly. There may be pain, cramp, tingling, heaviness and restless legs. On examination there might be obvious oedema, eczema, ulcers, haemosiderin, hemorrhage, phlebitis, atrophied blanch, lipodermatosclerosis.
Examination
Salpehna Varix Dilatation of the saphenous vein at its confluence with the femoral bein. It transits a cough impulse and may be mistake for an inguinal or femoral hernia. On closer examination it may have a bluish tinge.
An international consensus conference initiated the Clinical-Etiology-Anatomy-Pathophysiology (CEAP) classification to categorize chronic venous disorders
| C0 | No visible or palpable signs of venous disease |
| C1 | Telangiectases or reticular veins |
| C2 | Varicose veins |
| C3 | Oedema |
| C4 | Pigmentation, eczema, lipodermatosclerosis, atrophie blanche |
| C5 | Healed venous ulcer |
| C6 | Active venous ulcer |
| CA | Asymptomatic |
| CS | Symptomatic |
Patients with complications of varicose veins (CEAP 3–6); and those with clinical evidence of chronic deep vein insufficiency, especially venous eczema or ulceration, require referral to a vascular surgeon.
Education
Medical Treatment
Endovenous ablation is an image-guided, minimally invasive treatment for varicose veins. It uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize (burn) and close the varicose veins.
Surgical Treatment
Many patients are treated for cosmetic concerns alone, so it is important to manage patients’ expectations.
Complication of Varicose veins
Complications of surgery

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion