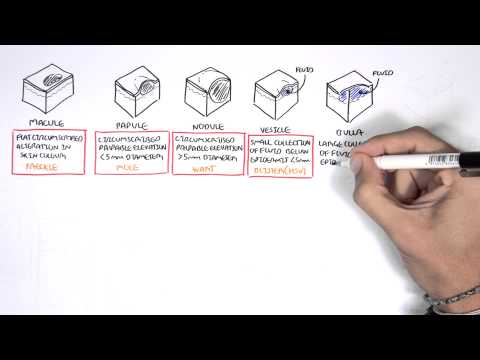
0:00 In this video, we're going to look at melanoma. 0:08 This is an overview of melanoma, an introduction. 0:13 Melanoma is cancer of the skin. 0:16 Melanoma has the highest mortality rate of all dermatological cancers. 0:22 Melanoma is also one of the most common cancers in young adults. 0:27 So what are some risk factors for developing melanoma? 0:31 Well, some common risk factors include having a family history of melanoma, 0:36 having a personal 0:37 history, having light hair color, light eye color, having a high freckle 0:44 density, being 0:45 immunosuppressed either because of the use of drugs or having a particular 0:51 disease, and 0:52 having multiple melanocytic nevi, essentially multiple moles. 0:59 So how does melanoma look like? 1:02 Well, melanoma looks different in each individual. 1:07 So let's zoom into this person's face. 1:09 And here is a cross-section of a skin with melanoma. 1:12 Let us compare this to a normal skin cross-section. 1:18 The top layer of our skin is known as the epidermis. 1:22 Below the epidermis is the layer called the dermis. 1:27 Below the dermis is another layer known as the hyperdermis, which contains sub 1:30 cutaneous 1:31 fat, which is important for thermoregulation. 1:35 As I mentioned, melanoma is different in each individual. 1:38 However, melanoma is usually always pigmented. 1:41 It's a pigmented lesion. 1:44 It's often asymmetric. 1:45 It has ill-defined borders, and melanoma often bleeds or ulcerates. 1:54 So how does melanoma develop? 1:57 We'll let us zoom into the epidermal layer of the normal skin and compare it to 2:03 the epidermal 2:03 layer of a skin with melanoma. 2:07 We are now looking at the pathology of melanoma. 2:11 Here are some cells that make up the epidermis. 2:15 Here again is our epidermal layer, and below the epidermis is our dermis. 2:20 In between the epidermis and the dermis is our basement membrane. 2:24 Essentially, this is what separates the epidermis to the dermis. 2:31 Just above the basement membrane, we have a special cell of the skin known as 2:37 melanocyte. 2:38 Melanocytes are important for us because they help protect us from UV radiation 2:43 , and they 2:44 help in our skin pigmentation. 2:49 In melanoma, what happens is we have proliferating melanocytes. 2:55 So these melanocytes that are normally harmless become mutated, and they grow 3:00 and divide rapidly, 3:01 resulting in melanoma. 3:04 These risk factors can lead to these proliferating melanocytes. 3:09 When going to a doctor and it's suspected of having melanoma, it is important 3:14 to examine 3:15 the skin lesion. 3:17 A good way to examine the skin lesion is to follow the A, B, C, D, E rule. 3:23 So in A, we look for asymmetry. 3:26 In B, we look for ill-defined borders. 3:29 In C, we look for any color changes, or even bleeding. 3:33 In D, we check for the diameter and possibly the depth. 3:37 And E, possibly the most important, is we look at elevation and in particular 3:43 evolution. 3:45 So if the skin lesion changes quickly or rapidly in the short duration, melan 3:50 oma is 3:51 suspected. 3:54 There are ways to prevent melanoma. 3:58 These include wearing a hat, using sunscreen, wearing long-sleeved shirts, 4:07 protective clothing, 4:08 especially if you work outside a lot, wearing sunglasses, and also if you have 4:14 a family 4:15 or personal history of melanoma having regular doctor skin checks or even self- 4:20 skin checks. 4:22 So that was an overview of melanoma. 4:25 Thank you for watching.