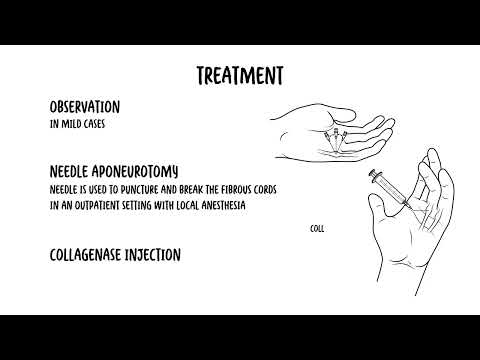
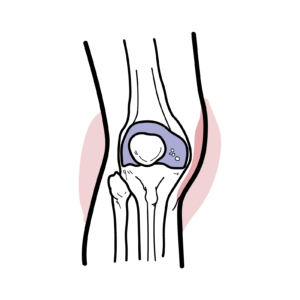
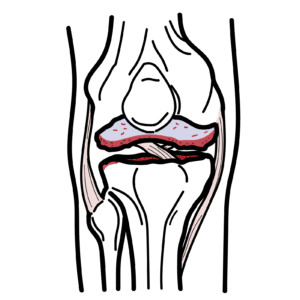
0:00 Trigger finger is a common condition which may cause significant functional 0:15 problems. 0:16 Trigger finger also known as the nosing flexotino sonovitis is a condition in 0:21 which the finger 0:22 or the thumb clicks or locks when inflection preventing a return to extension. 0:36 The long flexotendens of the fingers arise from the flexor digitorium 0:41 superficialis 0:43 and flexor digitorium profundis at the forearm muscles. These tendons enter the 0:50 hand via the 0:51 carpal tunnel enclosed in a common sinovial sheath. The role of the flexor dig 0:57 itorium tendon 0:59 is to perform flexion of the fingers, so forming a fist. Within the hand, the 1:06 tendons fan out 1:08 and enter via respective fibrous flexor sheaths. These sheaths are strong lig 1:15 amentous tunnels, 1:18 each associated with a digit. The sheath allows easy and smooth gliding 1:24 of the flexor tendon when flexing the fingers as shown in this diagram. 1:29 Now the fibrous flexor sheaths contain thickened areas known as the annular pul 1:39 leys. 1:39 These further support the tendon in place and are very important in the biome 1:45 chanics of finger 1:46 flexion. There are five annular pulleys which hold the tendon close to the bone 1:52 . The A1 pulley 1:54 at the level of the metacarpal head is the first part of the sheath and is 1:59 subject to the highest force. 2:01 As you can see, what happens first is you get inflammation of the flexor pulley 2:12 A1. 2:13 Over time, this can lead to inflammation of the flexor tendon underneath, 2:17 leading to a catching 2:19 sensation as the finger is bent. Inflammation can then lead to formation of a 2:25 nodule that, 2:27 when big enough, can lead to triggering of the finger. Here, you can see when 2:33 the fingers are 2:34 flexed, the nodule moves proximal to the pulley. However, when the person 2:40 attempts to extend 2:42 the digit, this nodule fails to pass back under the pulley. Consequently, the 2:49 digit becomes locked 2:50 in a flex position. This is a trigger finger. 2:54 Usually, trigger finger is painless and sometimes has complaints of catching, 3:06 locking, 3:06 or snapping of the finger. It can be corrected by bringing the finger and 3:10 extension with the other 3:11 hand. However, trigger finger can become painful over time. 3:15 Management involves splinting the triggered fingers and extension to allow rest 3:25 . If this does not help 3:27 or in cases of severe functional impairment, steroid injections can be trial, 3:33 which can show 3:34 improvement over a few days. Surgical management is also an option, a trigger 3:40 finger release, 3:41 via a needle, can be attempted in most cases, involving the release of the 3:47 tunnel using a needle 3:49 performed under local anaesthetic. 3:52 The main risk of developing trigger finger is over use of the flexor tendons 4:04 such as prolonged 4:06 gripping and the use of hands. Other risk factors include rheumatoid arthritis, 4:11 diabetes mellitus, female gender, and increasing age. 4:17 Differential diagnosis of trigger finger includes duperchine's contracture, 4:25 where you get thickening and contraction of the palmar fascia, causing a fixed 4:30 and painless 4:31 flexion deformity that cannot be passively corrected. 4:36 Infection within the tendons' sheets, usually preceded by a trauma, can also 4:46 cause painful, 4:47 swollen, erythematous digit. 4:50 A ganglion cyst is another differential involving the tendon she. 5:01 Acromegli, where you get excessive growth hormone, results in swelling of the 5:06 flexor 5:07 synovion within the tendon sheath due to increased extracellular volume. 5:11 So in summary, trigger finger is a common condition which may cause 5:20 significant functional impairment, also called stenosing flexotino-synovitis. 5:25 It is a condition 5:26 in which the finger, or thumb click or lock when inflection, preventing a 5:31 return to extension. 5:32 Thank you for watching.