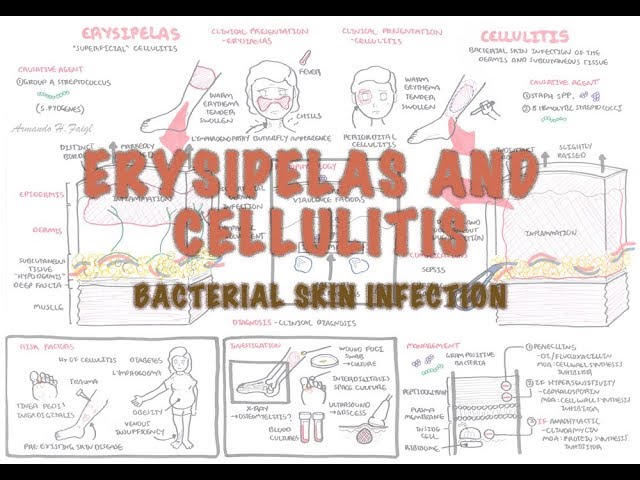
0:00 Bacteria in general can be divided into gram-negative and gram-positive 0:14 bacteria, depending on their 0:15 cell wall, their peptidoglycan makeup. 0:19 Gram-positive implies a thick peptidoglycan layer, and they stain a purple 0:25 color. 0:26 Now there are two main species of gram-positive cockeye that causes human 0:32 infections. 0:33 These are streptococci and staphylococci. 0:38 They are differentiated by two main criteria. 0:42 Firstly, their ability or inability to produce the enzyme catalase. 0:50 Staphylococcal species are catalase-negative, staphylococcal species are catal 0:56 ase-positive, 0:57 which allow them to convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. 1:03 Hence, on a slide or tube, bubbles are formed. 1:07 The second criteria to differentiate staphylococcus to streptococcus is based 1:12 on microscopic 1:13 appearance. Staphylococcus species are usually in clusters, whereas streptococ 1:20 cus species 1:21 are arranged in pairs or chains. 1:26 Striptococcal infections remain a serious health problem worldwide. 1:31 The streptococci are divided based on their oxygen requirement and are 1:35 classified into 1:36 erobes, facultative anaerobes, or obligate anaerobes. Forget about those terms, 1:43 here we 1:43 are focusing on aerobic and facultative anaerobics, which make up the majority 1:51 of streptococcus 1:52 species. I am writing aerobic here because facultative anaerobes are able to 1:59 survive an 2:00 oxygen as well. The gram-positive streptococci are then further divided into 2:08 the hemolytic 2:10 properties in blood. The streptococcus species are smeared in blood agar, which 2:18 is a plate 2:19 containing blood. Hemolytic properties of the bacteria means the bacteria's 2:26 ability to 2:27 hemolyse, to break down the red blood cells on the plate. Streptococci are 2:33 divided into 2:34 three hemolytic groups, alpha-hemolytic, beta-hemolytic, and gamma-hemolytic. 2:41 Alpha-hemolytic 2:42 is where the streptococci causes partial hemolysis. So on the blood agar, there 2:50 is a small area 2:51 around the bacteria that is smeared, which has cleared and displays a greenish 2:57 type color. 2:59 Partial hemolysis means some of the red blood cells on the plate have hemolyzed 3:04 . Beta-hemolysis 3:09 is where the streptococci causes complete hemolysis. So a certain circumference 3:16 around 3:16 where the streptococci was smeared on the plate will display clearing of the 3:21 red blood cells, 3:23 because these red blood cells have undergone hemolysis by the bacteria. Gamma- 3:29 hemolytic 3:30 streptococci do not hemolyze any red blood cells on the plate, and so the plate 3:34 is all 3:35 red. The red blood cells are still there. Once the hemolytic properties of the 3:41 streptococcus 3:42 species is identified, this narrows the type of streptococci. For example, the 3:49 two main 3:50 alpha-hemolytic streptococci's are streptococcus pneumoniae and streptococcus 3:57 viridians. 3:58 The two bacteria can be further differentiated by smearing the alpha-hemolytic 4:04 streptococci 4:05 in a medium with an optocean disc. Optocean is a derivative of a quinine. You 4:13 don't need 4:14 to know anything more about it. Streptococcus pneumoniae, the bacteria, which 4:19 is well known 4:19 to cause community acquired pneumoniae and acute otitis media, is susceptible 4:25 to optocean. 4:27 And so around the optocean disc, there is a space because all the streptococcus 4:33 pneumoniae 4:34 and the bacteria have died around it. But another feature of streptococcus 4:40 pneumoniae 4:41 is that they are a capsulated organism, they have a capsule. Streptococcus vir 4:46 idians, on 4:47 the other hand, is resistant to optocean and does not contain a capsule. And so 4:54 on this 4:55 plate surrounding the optocean disc, streptococcus viridians still exist 5:01 because they're resistant. 5:03 The beta-hemolytic streptococci are further classified based on antigenic 5:10 structure. 5:11 This is the Lancefield classification. The antigenic structure is a serological 5:17 classification 5:18 system and is based on the detection of specific carbohydrate antigens on the 5:24 cell wall of 5:25 the streptococci. The Lancefield classification include, basically, groups A to 5:32 W with the 5:33 exception of I and J. So for example, the majority and one of the most 5:40 important human 5:41 pathogens belong to group A in the Lancefield classification. These are called 5:47 the group 5:47 A streptococci, also known as streptococcus pyogenes. Streptococcus pyogenes is 5:54 the most 5:54 important human pathogen causing bacterial pharyngeitis, rheumatic heart 6:00 disease, and 6:01 post streptococcal glomerular nephritis, for example. Group B streptococcus is 6:06 also known 6:07 as streptococcus agalectae, well known for causing neo-natal infections. And 6:13 the group 6:14 B streptococcus is the bacteria screened in pregnant women. The gamma-hemolytic 6:20 streptococci 6:21 are the interococci, and these include the interococcus faecalis and the inter 6:25 ococcus 6:26 feet fetium. These guys are normally found in the gastrointestinal tract, hence 6:33 feces, 6:34 and are also classified under the Lancefield classification as group D strept 6:39 ococcus. 6:40 I hope you enjoyed this video on the overview of the streptococcal. I hope you 6:47 enjoyed this video 6:49 of the overview of streptococcus species. Later videos will look into the 6:55 different types 6:56 of streptococcus species, specifically streptococcus pyogenes, for example, 7:02 and streptococcus pneumonia.