Sexual Transmitted Infection
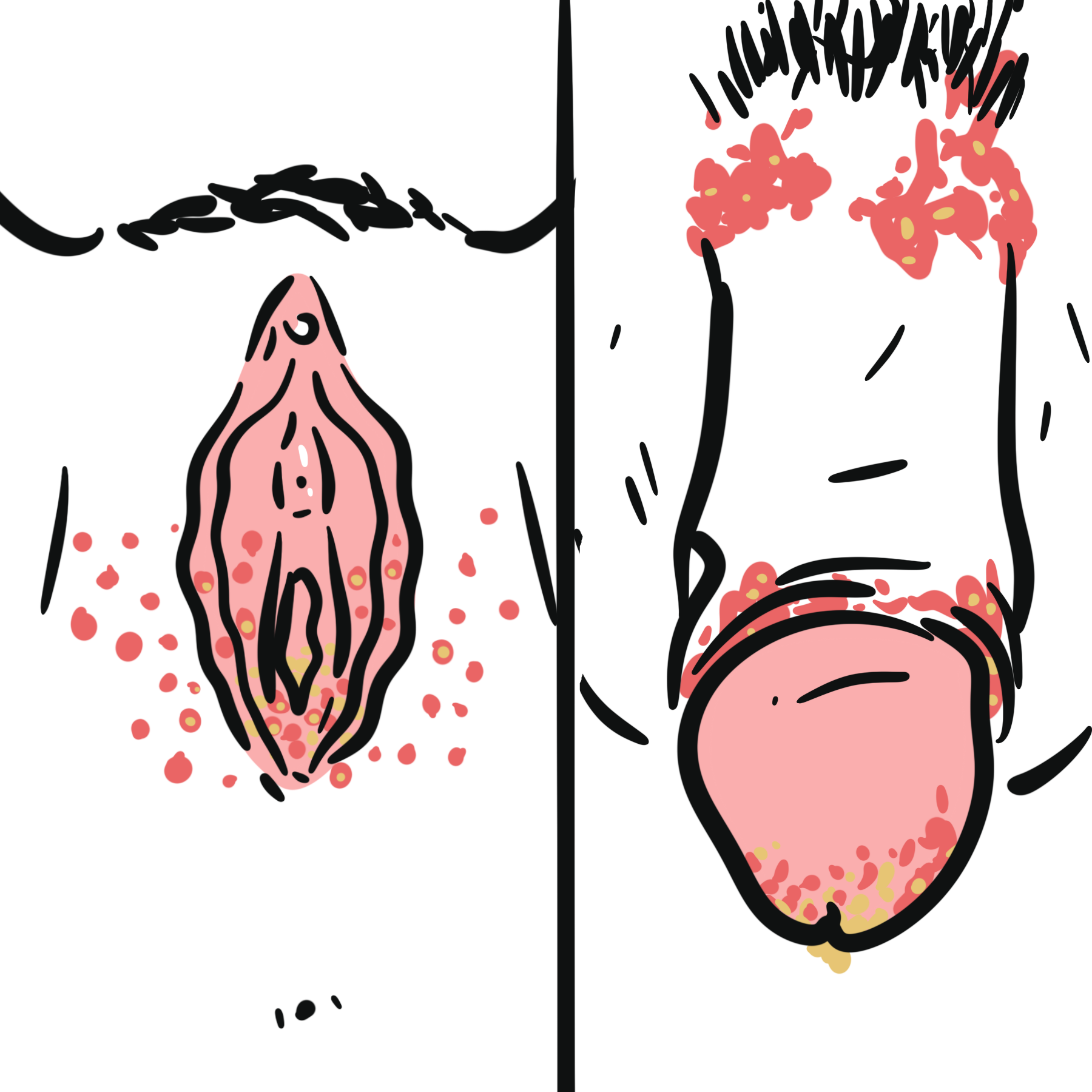

Sexually transmitted infections (STI) are a significant public health worldwide. STI can result in chronic disease, pregnancy complications, infertility, and even death. Globally, congenital syphilis is still a leading cause of stillbirth and neonatal death. Antibiotic-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae continues to be a significant public health concern. Chlamydia trachomatis infection is the most frequently reported sexually transmitted infectious disease in the United States and continues to be an important risk factor for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ectopic pregnancies, urethritis, cervicitis, chronic pelvic pain, and infertility. Treatment of STDs should also include treatment of patients’ partners. Overall, patients, especially the younger population, should be screened regularly and counselled to ensure early diagnosis and treatment. Contraception does not prevent STI, protection such as condoms do.
STI: Infections that can be spread during sexual contact, some infections like herpes and warts can also be transmitted by skin to skin contact
Contraception: Deliberate use of artificial methods or other techniques to prevent pregnancy as a consequence of sexual intercourse. Methods include barrier methods, contraceptive pill and intrauterine devices. Only the barrier method can prevent STIs
Sex Protection: Safe sex is having sexual contact while protecting yourself and your sexual partner against sexually transmissible infections (STIs) and unplanned pregnancy.
Vaginal swab: First-line investigation for suspicion of STI. You can perform high vaginal swab, low vaginal swab or swab from the cervix itself.
Nucleic acid amplification test: Nucleic acid amplification is a valuable molecular tool not only in basic research but also in application oriented fields, such as clinical medicine development, infectious diseases diagnosis, gene cloning and industrial quality control. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was the first nucleic acid amplification method developed and until now has been the method of choice.
PCR: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was the first nucleic acid amplification method developed.
Pap smear: Quick and simple test used to check for changes to the cells of the cervix that may lead to cervical cancer.
Premenarche female with signs of STD – sexual abuse?
| Notifiable STI in Australia |
| Chlamydia |
| Donovanosis |
| Gonorrhoea |
| Syphilis |
| Hepatitis |
| HIV |
| Characteristic of common cause of vaginal discharge | |||
| Appearence | Smell | Itch | |
| Physiological | Clear/white, mucoid | – | – |
| Foreign body | Grey or bloody, purulent | Offensive | – |
| Malignancy | Bloody, watery | Offensive | – |
| Bacterial Vaginosis | Grey, watery | Offensive | Itchy |
| Trichomonas | Green, frothy | Offensive | – |
| Candidasis | Curd like (cheesy) | – | Itchy |
| Gonococcal | Green, watery | – | – |
| Risk Factors |
| Unprotected intercourse without male or female condom use |
| Unprotected mouth-to-genital contact |
| Early sexual activity, especially before age 18 |
| Having multiple sex partners |
| Having a high-risk partner (one who has multiple sex partners or other risk factors) |
| Having anal sex or a partner who does |
| Alcohol and Illicit Drug use |
| Exchange of sex (sex work) for drugs or money |
Approach
It is important to note notifiable sexually transmitted infections and also CONTACT TRACING!
Although initial treatment of simple infection may be appropriate without culture, symptomatology can be variable and the gold standard should be a positive culture and sensitivity, especially with persistent or recurrent symptoms.
Overview
Diagnosis
Treatment
Overview
Clinical Presentation
| Characteristic of common cause of vaginal discharge | |||
| Appearence | Smell | Itch | |
| Physiological | Clear/white, mucoid | – | – |
| Foreign body | Grey or bloody, purulent | Offensive | – |
| Malignancy | Bloody, watery | Offensive | – |
| Bacterial Vaginosis | Grey, watery | Offensive | Itchy |
| Trichomonas | Green, frothy | Offensive | – |
| Candidasis | Curd like (cheesy) | – | Itchy |
| Gonococcal | Green, watery | – | – |
Diagnosis
Treatment
Metronidazole is a prodrug. Unionized metronidazole is selective for anaerobic bacteria due to their ability to intracellularly reduce metronidazole to its active form. This reduced metronidazole then covalently binds to DNA, disrupt its helical structure, inhibiting bacterial nucleic acid synthesis and resulting in bacterial cell death. Metronidazole is used against protozoa such as Trichomonas vaginalis, amebiasis, and giardiasis. Metronidazole is extremely effective against anaerobic bacterial infections and is also used to treat Crohn’s disease, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and rosacea.
Complications
In pregnancy Trichomonas infection is associated with preterm delivery and low birth weight baby.
Overview
Clinical Presentation
Diagnosis
Treatment
In pregnancy chlamydia infection is associated with preterm rupture of membranes. Risks to the baby include neonatal conjunctivites and pneumonia.
Complications
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome is a rare complication of Pelvic inflammatory disease which involves liver capsule inflammation leading to the creation of adhesions.
Reiter’s syndrome also known as reactive arthritis presents with the classic triad: conjuctivities, urethritis and arthritis. (Can’t see, can’t pee, can’t climb a tree).
Overview
Clinical Presentation
| Characteristic of common cause of vaginal discharge | |||
| Appearence | Smell | Itch | |
| Physiological | Clear/white, mucoid | – | – |
| Foreign body | Grey or bloody, purulent | Offensive | – |
| Malignancy | Bloody, watery | Offensive | – |
| Bacterial Vaginosis | Grey, watery | Offensive | Itchy |
| Trichomonas | Green, frothy | Offensive | – |
| Candidasis | Curd like (cheesy) | – | Itchy |
| Gonococcal | Green, watery | – | – |
Diagnosis
Antibiotic-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae continues to be a significant public health concern.
Treatment
In Pregnancy the risk of gonorrhoea infection to the baby is opthalmia neonatarum (50% of cases).
Complications
Bartholin’s abscess (cyst) The bartholin glands are located bilaterally at the base of the labia minora. Obstruction of the distal Bartholin’s duct may result in the retention of secretions, with resultant dilation of the duct and formation of a cyst. The cyst may become infected, and an abscess may develop in the gland. A Bartholin’s duct cyst does not necessarily have to be present before a gland abscess develops.
Overview
Clinical Presentation Syphilis can present in one of latent different stages
| STDS with Ulcers |
| Chancroid (Painful) |
| Syphilis (Painless |
| Herpes (Painful) |
Diagnosis
Treatment
Complications
In Pregnancy syphilis infection can result in preterm delivery, stillbirth, congenital syphilis and miscarriage.
Overview
Clinical Presentation
| Characteristic of common cause of vaginal discharge | |||
| Appearence | Smell | Itch | |
| Physiological | Clear/white, mucoid | – | – |
| Foreign body | Grey or bloody, purulent | Offensive | – |
| Malignancy | Bloody, watery | Offensive | – |
| Bacterial Vaginosis | Grey, watery | Offensive | Itchy |
| Trichomonas | Green, frothy | Offensive | – |
| Candidasis | Curd like (cheesy) | – | Itchy |
| Gonococcal | Green, watery | – | – |
Diagnosis – Amsel criteria 3 out of 4 required
| Amsel criteria |
| Homogenous whitish grey discharge |
| Vaginal pH >4.5 (5.5?) |
| Fishy smell of vaginal discharge |
| Presence of ‘clue cells’ on microscopy |
Treatment
Complications
In pregnancy bacterial vaginosis is associated with mid-trimester miscarriage, preterm rupture of membranes and preterm delivery.
Overview
Clinical Presentation
| Characteristic of common cause of vaginal discharge | |||
| Appearence | Smell | Itch | |
| Physiological | Clear/white, mucoid | – | – |
| Foreign body | Grey or bloody, purulent | Offensive | – |
| Malignancy | Bloody, watery | Offensive | – |
| Bacterial Vaginosis | Grey, watery | Offensive | Itchy |
| Trichomonas | Green, frothy | Offensive | – |
| Candidasis | Curd like (cheesy) | – | Itchy |
| Gonococcal | Green, watery | – | – |
Diagnosis
Treatment
Azole inhibit fungal inhibitis enzymes responsible for the synthesis of ergosterol. Ergosterol is an essential component of the fungal cell membrane, inhibition of its synthesis results in increased cellular permeability causing leakage of cellular contents. Side effects: symptoms of overdose include hallucinations and paranoid behavior.
Complications
Overview
Clinical Presentation
Diagnosis
Treatment
Aciclovir is an antiviral drug that acts as an antimetabolite, inhibits DNA synthesis by acting as a chain terminator. Aciclovir is used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, varicella zoster (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles). Side effects: Nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity, which usually resolve after cessation of aciclovir therapy.
Complications
In pregnancy herpes infection can lead to neonatal herpes a rare, but sometimes fatal, condition that can occur when an infant is exposed to HSV in the genital tract during delivery.
Overview
Clinical Presentation – condyloma accuminatum
Diagnosis
Treatment for genital warts
Complications
Drugbank.ca
CDC
Oxford Handbook of Obstetrics and Gyaenacology

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion