Cough

Coughing is a protective reflex, a component of normal respiratory function, it enables irritants and foreign bodies to be expelled from the vulnerable respiratory tract, however it can also be voluntarily generated and therefore has non-reflex elements to assist/enhance with mucocilliary clearance.
| Defintion Acute cough: present up to 14 days/2 weeks Prolonged acute cough: lasting 2 – 3 weeks Chronic cough: present > 3 weeks |
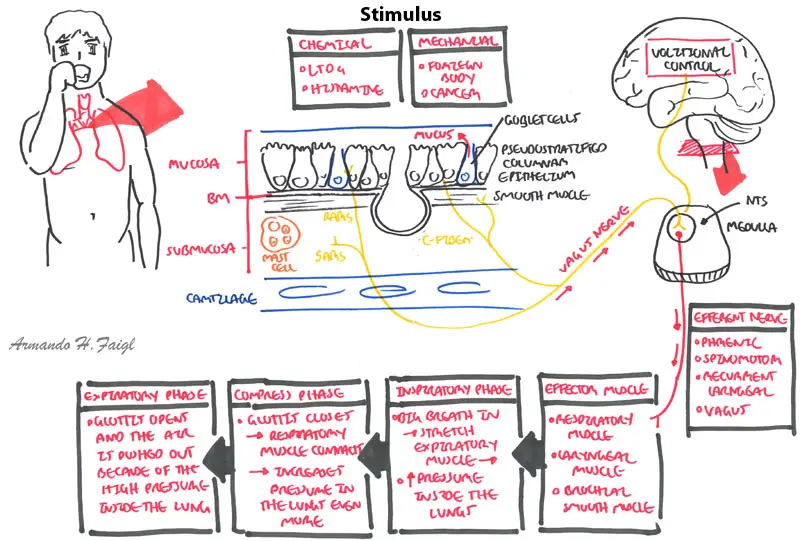
| Watch Video: Physiology of Cough |
The anatomical structures of the respiratory tract are very sensitive structures.
| Alarm symptoms |
| Prominent dyspnoea, esp. at night or rest |
| Recurrent episodes of chronic wet or productive cough |
| Systemic Sx: fever, anorexia, wt. loss, failure to thrive |
| Feeding difficulties inc. choking or vomiting |
| Recurrent pneumonia |
| Additional breath sounds |
| Abnormal clinical respiratory examination |
| Abnormal CXR |
| COMMON CAUSES OF COUGH | ||||
| Conditions | History | Examination | Workup | Aetiology |
| Asthma | Expiratory wheeze | Oxygen, Fluids, bronchodilators +/-inhaled corticosteroids (depends on severity) | Infection | |
| Foreign body | Sudden onset, history of choking | Cough, Stridor | CT, bronchoscopy | Foriegn Body |
| Viral bronchiolitis | Coryzal symptoms (2-3 days) followed by respiratory distress | Fine inspiratory crackles, expiratory wheeze, fever | Usually non required | RSV |
| Acute URTIs | Coryzal symptoms | |||
| Allergic rhinitis | ||||
| Croup (laryngotracheobronchitis) | Barking cough, coryza | Low-grade fever, nasal flaring, respiratory retractions, stridor | Generally not indicated | Generally not indicated |
| Remember Young children develop 6-12 respiratory tract infections per year, usually accompanied by cough. In most children the cough is self-limiting (1-3) weeks. |
| CAUSES OF CHRONIC COUGH | ||||
| Condition | History | Examination | Workup | Aetiology |
| Smoking Exposure | Smoking exposure | Not significant | Generally not indicated | Smoking |
| GOR/GER | Heartburn present, or if cough is worse at night or after eating specific foods | |||
| Sinusitis | Nasal discharge, obstruction, toothache, unilateral facial pain, headache, fever “Sinusitis is not associated with cough” | Tender sinuses, fever, inflamed nasal mucosa, pus exudating from middle meatus, maxillary transillumination | ||
| Post-nasal drip | ||||
| Bronchiectasis | ||||
| Remember The most common causes of chronic cough in children are asthma, respiratory tract infections, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. |

Well child, normal examination
Unwell child or abnormal examination

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion