Giardiasis overview
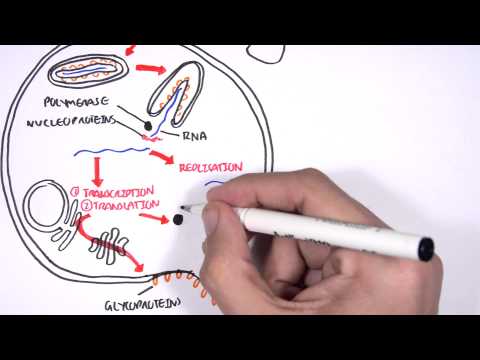
Giardiasis causes watery, greasy diarrhea, bloating, and weight loss—learn how Giardia lamblia is transmitted, diagnosed, treated, and prevented to protect yourself and vulnerable populations. In this concise video you’ll discover the Giardia life cycle (cysts and trophozoites), common transmission routes (fecal-oral, contaminated water and food), and why half of infections can be asymptomatic.
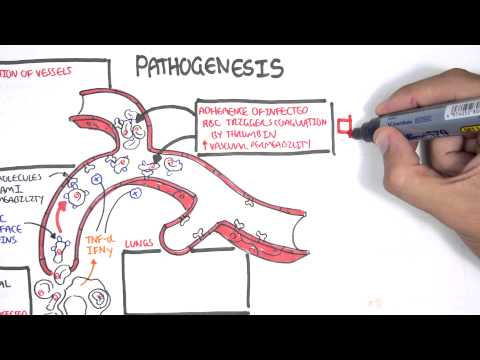
Watch to understand the clinical signs—foul-smelling, frothy stools, abdominal cramps, nausea, dehydration, and potential long-term effects like lactose intolerance, reactive arthritis, or growth delays in children. The video explains pathophysiology: how Giardia disrupts gut microvilli, impairs nutrient absorption, alters the microbiome, and evades immunity via surface antigen changes. Learn who’s at higher risk—children, travelers, those with poor sanitation, immunocompromised people, and childcare workers—and why treating even asymptomatic cases can prevent spread to high-risk groups.
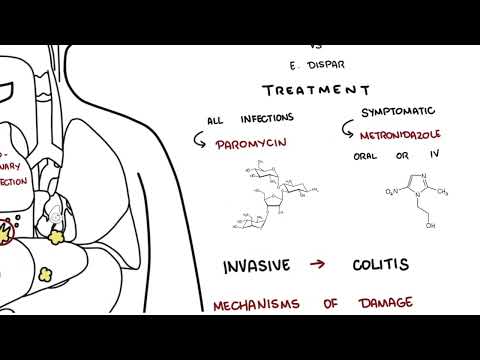
Get clear guidance on diagnosis: stool microscopy, antigen enzyme immunoassays, stool PCR, and endoscopic sampling for duodenal trophozoites—plus the limitations of each test. Treatment-focused segments cover first-line antimicrobials like metronidazole and other nitroimidazoles, plus fluid and electrolyte support. Practical prevention tips include safe water treatment, hygienic food handling, handwashing, avoiding untreated wilderness water, and improving nutrition (zinc, vitamin A) in resource-limited settings.
Whether you’re a healthcare professional, traveler, or caregiver, this video equips you with actionable knowledge to recognize, manage, and prevent giardiasis. Watch now to safeguard health and reduce transmission risks.