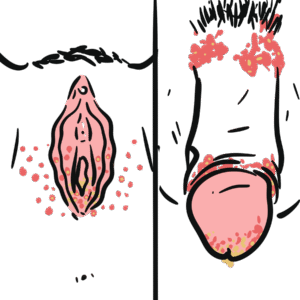
0:00 Hello, in this video, we're going to talk about Niceria gonorrhea. 0:09 Niceria gonorrhea is a gram negative diplococci, which causes gonorrhea, a 0:14 sexually transmitted 0:15 infection, which, if left untreated, can cause serious complications such as se 0:20 ptic arthritis 0:21 and pelvic inflammatory disease. 0:24 Niceria is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection 0:29 worldwide, 0:30 after chlamydia. 0:32 Rates of gonorrhea infection have been increasing thanks to the emergence of 0:36 broad spectrum antibiotic 0:38 resistant organisms. 0:42 Let's talk about the life cycle of Niceria gonorrhea. 0:46 Niceria gonorrhea is a gram negative, obligate, fastidious diplococcus bacteria 0:52 . 0:52 Like all gram negative bacteria, Niceria gonorrhea possesses a cell envelope, 0:57 which 0:58 is composed of an inner cytoplasmic membrane, a middle layer of peptidoglycan 1:04 and an outer 1:05 membrane. 1:07 The outer membrane contains lipo oligosaccharides, or LOS, which is an endot 1:16 oxin. 1:17 The outer membrane also contains the phospholipid and a variety of proteins 1:21 that contribute 1:22 to cell adherence, tissue invasion, and resistance to host defenses. 1:30 Niceria gonorrhea has many dynamic polymeric protein filaments, called pili, 1:37 which allow 1:38 the bacteria to adhere to and move along surfaces of cells. 1:47 Niceria gonorrhea is transmitted sexually, either oral, genital, or anal roots. 1:54 Niceria gonorrhea can also be transmitted perinatally, from mother to infant. 2:01 Risk factors for Niceria gonorrhea, and its infection, include age 20 to 29, 2:10 having multiple 2:11 sexual partners, having unprotected sex, having known partners with gonorrhea, 2:17 men who have 2:17 sex with men, current or prior history of sexual transmitted infections. 2:25 Let's talk about the pathophysiology of Niceria gonorrhea, and how it causes 2:30 all the complications 2:31 associated with it. 2:34 Firstly, the acquisition of Niceria gonorrhea is through sexual contact, mainly 2:40 as we have 2:41 learned. 2:42 Niceria gonorrhea infects primarily columnar epithelial cells. 2:48 In this scenario, it is in the urethra or the vaginal epithelium. 3:00 The pili of the Niceria gonorrhea attaches and adheres to the columnar epit 3:05 helial cells. 3:07 Adheres to the cells is also facilitated by opacity proteins, termed opa 3:13 proteins. 3:14 Niceria gonorrhea have many virulent factors, really things that help them with 3:20 their infection. 3:21 The gonococcal lipo oligosaccharide, the LOS, is an endotoxin, and causes sili 3:28 ostasis and 3:30 sloughing of ciliated epithelial cells, basically damaging the cells. 3:36 Multiple oligosaccharides also activates complement and immune cells, such as 3:41 the macrophages and 3:42 neutrophils, which also contributes to the acute inflammatory response. 3:49 Niceria gonorrhea have something called IgA protease. 3:54 This enzyme inactivates the host immunoglobulins IgA by cleaving the molecule 3:59 in the hinge region, 4:01 allowing the bacteria to pass this area without any problems. 4:07 Niceria gonorrhea also has a capsule, which helps evade phagocytosis, basically 4:12 hide 4:12 or not be phagocytized by the macrophages and neutrophils. 4:18 They also contain pore and proteins, termed pore proteins, which help evade 4:23 immune system. 4:26 All these virulent factors help essentially with niceria gonorrhea entering the 4:31 cell, 4:31 that helps the bacteria with mucosal invasion whilst evading the immune system. 4:38 Mucosal invasion by niceria gonorrhea results in a local inflammatory response 4:45 that produces 4:46 a purulent exudate. Transmission can subsequently occur to another patient with 4:52 through sexual contact. Lipo oligosaccharides attaches to sperm cells 4:59 and likely leads to transmission from males to uninfected sexual partners. 5:05 Niceria gonorrhea may ascend the urogenital tract and cause complications. 5:14 So in men, niceria gonorrhea causes urethritis, epi-dinnemitis and prostatitis. 5:25 Symptoms in men occur in more than 90% of infections and this will manifest as 5:32 urogenital 5:33 gonorrhea. Males will describe dysuria with urethritis, purulent urethral 5:40 discharge, 5:40 yellow and green in color. They may also complain of abdominal discomfort. 5:45 [Silence] 5:52 When niceria gonorrhea causes infection in the urogenital tract in females, 5:58 they can cause acute endometritis, salpangitis, which is inflammation of the 6:03 fallopian tubes and acute pelvic inflammatory disease. These conditions may 6:10 lead to infertility 6:12 long term, chronic pelvic pain and ectopic pregnancy. Niceria gonorrhea can 6:18 also 6:19 disseminate from the fallopian tubes through the peritoneum to the liver 6:24 capsule, 6:24 resulting in something called perihepatitis, termed Fitzhue Curtis syndrome. 6:29 Symptoms of urogenital gonorrhea in females occur only in 50% of cases and many 6:38 will not 6:38 manifest the symptoms interestingly. In females, symptoms include 6:44 serviceitis, which is inflammation and pain in the cervix. They also have 6:50 perlite cervical discharge, yellow and melodorous. Diceria, as well as 6:56 abdominal pelvic pain. 6:58 [Silence] 7:03 Niceria gonorrhea may invade the lymphatics and blood vessels as well 7:08 and this can cause other complications, including inguinal limb fatanopathy, 7:13 perineal perineal, ischorectal and periprostatic abscess for example, 7:20 endocarditis, as well as disseminated gonococcal infection, which is 7:29 characterized by the classic 7:31 triad, hemorrhagic vesicopostula eruption, polyothrologia, and tino-synovitis. 7:38 Other complications can also occur in the eyes. This typically occurs in 7:44 newborn babies, 7:46 as they are prone to eye infection if their mother has a gonorrhea infection. 7:50 Eye infection can cause permanent blindness, if not treated quickly. 8:01 Differential diagnosis of niceragonary infections are really other sexually 8:03 transmitted pathogens, 8:06 including chlamydia trachomitis, trachomonas vaginalis, and microplasmid 8:12 genitalium. 8:13 Investigations and diagnosis is through nucleic acid amplification test or NAT. 8:21 This test is done of a urine, of the urethral or cervical discharge. 8:31 Bacteria cultures can also be done of fluid from the cervix, from the blood, if 8:40 it's 8:40 there is disseminated infection, of the pharynx and joint. 8:44 Treatment of gonorrhea is with keftraxone and with the addition possibly of az 8:55 ithromycin 8:57 or doxycycline. It's important to have no sexual contact for several days after 9:03 treatment is 9:04 administered. There should be no sex with partners from the last two months 9:08 until the 9:09 partners have been tested and treated, if necessary. 9:12 So in summary, niceragonaria is a gram negative diplococci, which causes gonorr 9:19 hea, 9:20 a sexually transmitted infection that is common. Niceragonaria have many 9:25 virulent factors, including lipo oligosaccharides, 9:29 IgA proteases, and a capsule. They're able to evade the immune system and cause 9:39 infection 9:39 locally in the urogenital tract, or they can disseminate to the liver or to the 9:45 joint, 9:46 as well as causing disseminated gonococcal infection with the classic triad we 9:52 talked about. 9:54 Treatment is with antibiotics, such as keftraxone and azithromycin. 9:58 Thank you for watching.