Miscarriage
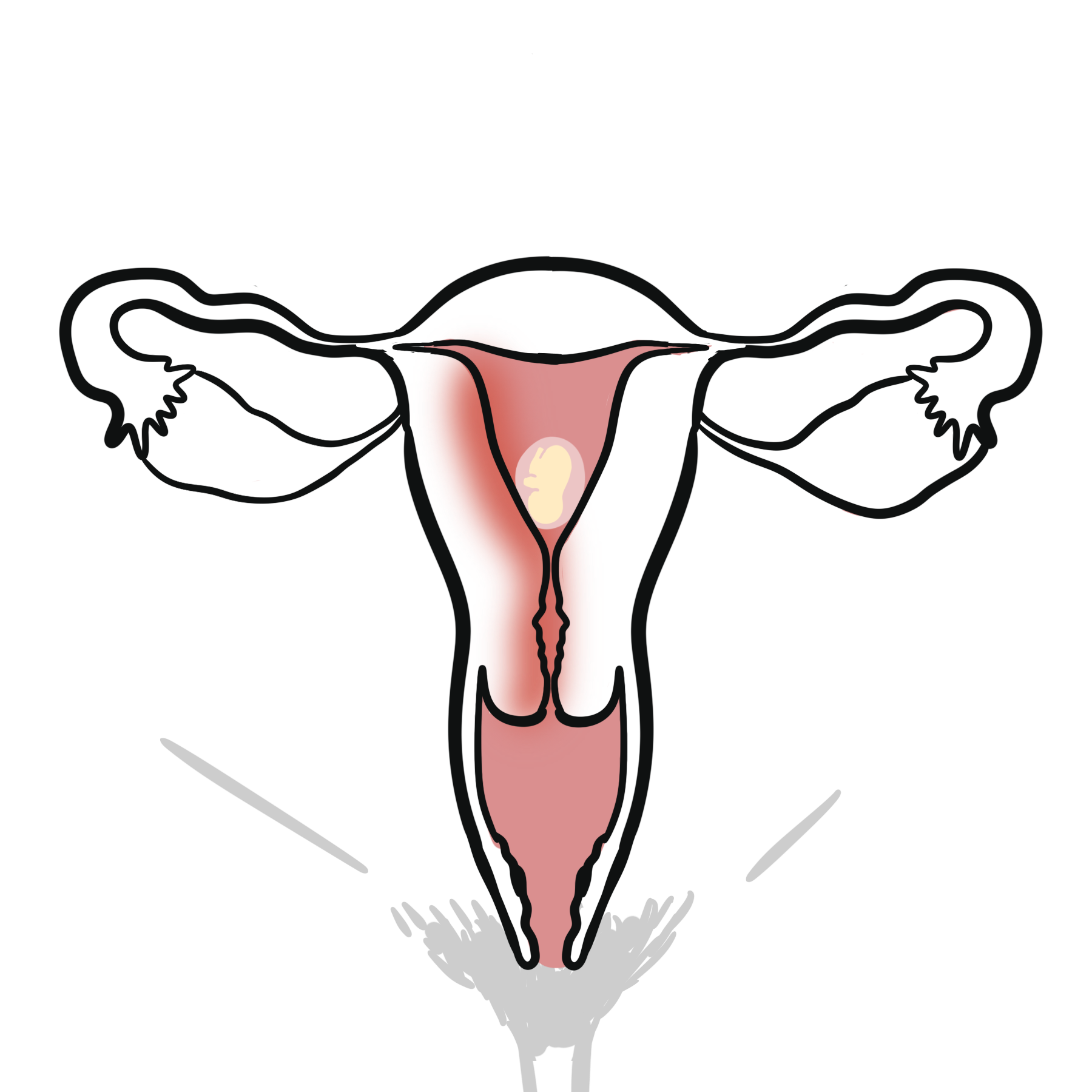

Miscarriage: Spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage, is defined as a clinically recognized pregnancy loss before the 20th week of gestation. Others define it as expulsion or extraction of an embryo or fetus weighing 500 g or less
Abortion: After 20weeks
Threatened miscarriage: A pregnancy less than 20 weeks’ gestation associated with vaginal bleeding, generally without cervical dilation.
Inevitable miscarriage: A pregnancy less than 20 weeks’ gestation associated with cramping, bleeding, and cervical dilation; there is no passage of tissue.
Incomplete miscarriage: A pregnancy less than 20 weeks’ gestation associated with cramping, vaginal bleeding, an open cervical os, and some passage of tissue per vagina, but also some retained tissue in utero. The cervix remains open due to the continued uterine contractions; the uterus continues to contract in an effort to expel the retained tissue.
Completed miscarriage: A pregnancy less than 20 weeks’ gestation in which all the products of conception have passed; the cervix is generally closed. Because all the tissue has passed, the uterus no longer contracts, and the cervix closes.
Missed miscarriage: A pregnancy less than 20 weeks’ gestation with embryonic or fetal demise but no symptoms such as bleeding or cramping.
Ectopic Pregnancy: Pregnancy outside of the normal uterine implantation site. Most of the time, this means a pregnancy in the fallopian tube.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin: “The pregnancy hormone,” which is a glycoprotein that is secreted by the chorionic villi of a pregnancy. It is the hormone on which pregnancy tests are based. The normal pregnancy will have a logarithmic rise in early pregnancy. Usually the β-subunit is assayed to prevent cross-reactivity with LH.
| Terminology | History | Substance | Cervical Os | Viability | Treatment |
| Threatened | Vaginal bleeding | No | Closed | Uncertain | Transvaginal ultrasound and hCG levels |
| Inevitable | Cramping, bleeding | No | Open | Abortion is inevitable | D&C vs expectant management |
| Incomplete | Cramping, bleeding | Some but not all tissues passed | Open | Nonviable | D&C |
| Complete | Cramping bleeding | All tissues passes | Closed | Nonviable | Follow hCG levels to negative |
| Missed/delayed | No symptoms | No | Closed | Nonviable | D&C vs expectant management |
Miscarriage is most commonly caused by chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo or exposure to teratogens. Very difficult to tell what cause was in each individual case.
Fetal Factors
Maternal factors
Fetal alcohol syndrome is the term given to a set of physical, mental and neurobehavioral birth defects caused by maternal alcohol consumption, during pregnancy.
Clinical Presentation
Importance of early bleeding in pregnancy:
Examination
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease An unusual type of abnormal pregnancy also known as molar pregnancy, which is trophoblastic tissue, or placenta-like tissue, usually without a fetus. The clinical presentation of molar pregnancy is vaginal spotting, absence of fetal heart tones, size greater than dates, and markedly elevated HCG levels.
With any early pregnancy bleeding rule out ectopic pregnancy.
Investigation
If a live embryo s seen on ultrasoundscan and the cervix is closed, the is reassired and follow-up is orgnaised. Complex platient may require serial β-hCG.
Other Investigations
Diagnosis Transvaginal ultrasound and beta-hCG supported by clinical evaluation.
Investigation – to identify a miscarriage and to differentiate between the types
Types of miscarriage
Conservative/expectant management
Medical management – Prostaglandins
Prostagladin analogues (misoprostol) work by induce uterine contractions and evacuate uterus contents.
Surgical management
Miscarriage can be very distressing for both the mother and partner. Consider support and counseling.
Dilatation and curettage refers to the dilatation of the cervix and scrapping of the parts of the uterine lining. It is both therapeutic and treatment for miscarriage.
Complication of Surgical Management of Miscarriage
Women with recurrent miscarriage should be referred to specialised services with expertise in dealing with recurrent pregnancy loss.

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion