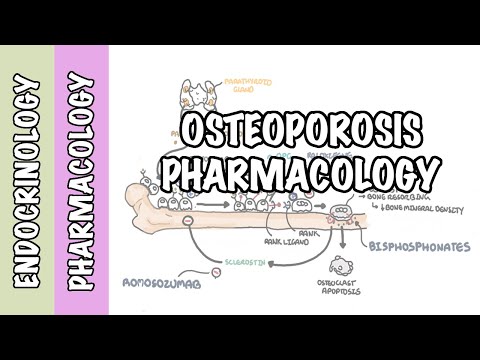
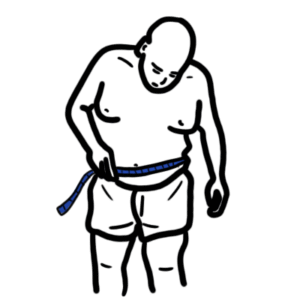
0:00 Obesity is defined as excess fat with many associated comorbidities, it is 0:11 associated 0:12 with a significant increase in mortality including a reduced life expectancy of 0:17 up to 10 years. 0:19 The body mass index or BMI is the accepted standard measure of obesity and 0:30 weight. 0:31 The BMI is represented by kilograms per meter squared. 0:35 Being underweight has a BMI of less than 18.5, a normal BMI is 18.5 to 24.9, 0:44 overweight 0:45 is 25 to 29.9, and obesity is greater than 30, which is then further divided 0:51 into three 0:52 different classes. 0:58 Another measurement of obesity is waist circumference, which takes into account 1:02 central adiposity 1:04 and really has a better correlation to cardiovascular disease. 1:08 Obesity is defined when the waist circumference in men is greater than 102 1:12 centimeters or greater 1:14 than 40 inches. 1:15 In women greater than 85 centimeters or 35 inches, the waist circumference is 1:24 measured 1:25 at the level of the iliac crest. 1:30 Obesity is complex and the pathophysiology involves genetics and behavioral 1:35 habits. 1:36 There is energy intake versus energy expenditure, as well as changes in the 1:41 neuroendocrine pathways. 1:44 But to put it simply, really, obesity occurs when you have increased energy 1:49 intake but 1:49 reduced expenditure. 1:51 And so all this accumulation of energy just goes into fat deposits around the 1:58 body. 1:59 The etiologies and risk factors of obesity can be divided into behavioral 2:05 things such 2:05 as physical inactivity, poor diet such as high takeaway foods, also cessation 2:15 of smoking 2:16 because people take up other habits such as eating more, further poor eating 2:21 patterns 2:21 such as overeating, binge eating or night eating is associated with increased 2:27 energy intake. 2:29 Slip deprivation is also a risk factor. 2:33 There are many medical causes of obesity. 2:36 These include hypothalamic obesity caused by damage to the hypothalamus, a part 2:39 of the 2:40 brain that makes hormones that control specific body functions such as sleep as 2:46 well as hunger. 2:47 Growth hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism, low thyroid levels released from the 2:53 thyroid 2:54 gland, hypogonadism. 2:57 In woman, polycystic ovarian syndrome, which is also associated with hercetism, 3:03 cushing 3:03 syndrome is a very important medical cause and really patients manifest with 3:09 elevated 3:09 cortisol levels and you could get moon-like facies and a buffalo hump. 3:14 There are many medications that can cause increase in weight. 3:18 These include namely corticosteroids, which really lead to cushing's appearance 3:23 and stimulates 3:24 appetite so you eat more, antipsychotics, antidepressants, beta blockers. 3:33 There are also anti-diabetic agents such as insulin which causes mild weight 3:38 gain as 3:39 well as sulfonal ureas. 3:48 Opens of obesity is a lot and these include stroke, the stigma associated with 3:53 being obese, 3:55 respiratory issues such as obstructive sleep apnea, obesity, hypoventilation 4:01 syndrome, 4:01 which is really characterized when you have slightly increased amounts of 4:04 carbon dioxide 4:05 in the body, gastroesophageal reflux disease, heart diseases including heart 4:13 attacks, hypertension, 4:15 hyperlipidemia, a fatty liver disease, diabetes, urinary incontinence, osteo 4:25 arthritis from 4:27 all the weight, increased risk of gout, venous thrombosis, hernias, as well as 4:36 an increased 4:37 risk of certain malignancies as well. 4:42 Number 2 know something called metabolic syndrome which really encompasses 4:47 obesity as well. 4:48 Metabolic syndrome describes a constellation of medical condition which 4:51 increases the risk 4:51 of cardiovascular disease. 4:54 These conditions include insulin resistance, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and 4:59 obesity, 5:00 all this make up metabolic syndrome. 5:06 The treatments for obesity, well, there's many approaches but first is to 5:09 address the 5:10 underlying cause if it's medical or behavioral as well as addressing the 5:16 triggers. 5:17 You want to set a realistic goal, for example, 5% body weight reduction per 5:22 year and good 5:23 idea to create an action plan involving a certain diet such as a low calorie 5:29 diet, an 5:29 exercise program, pharmacotherapy or medications also have a role in the 5:37 treatment of obesity. 5:39 Basically when all other things fail. 5:42 These pharmacotherapies include a GLP1 agonist, now a GLP1 is a normal peptide 5:47 that's produced 5:48 by the body which slows gastric emptying, inhibits glucagon excretion and 5:54 stimulates 5:55 insulin production. 6:00 The side effects of this include nausea and vomiting. 6:03 Further, GLP1 agonists are given as an injection into the tummy or the thigh 6:08 and so this could 6:09 also be a sort of side effect in a way. 6:13 Orolistat is another medication that works on the pancreas by inhibiting the 6:17 pancreatic 6:17 lipase. 6:20 Lipase is an enzyme which helps break down fat so that fat can be absorbed by 6:24 the body. 6:25 By inhibiting fat absorption you're essentially preventing fat accumulation. 6:30 The side effects of Orolistat include gastrointestinal upset as well as the a 6:36 teria, a fatty stool. 6:40 Sympethometics can also be used for the treatment of obesity and these include 6:40 fenteramine. 6:46 Sympethometics really, they increase the sympathetic activity in your body and 6:50 so your 6:50 fight or flight response and so you increase energy expenditure. 6:58 Another very, very important treatment for obesity is bariatric surgery and 7:03 there are 7:04 many types, there's the adjustable gastric band so it really suppresses 7:11 appetite by 7:12 really, you know, reducing the amount of food that you can actually take into 7:17 your stomach. 7:18 There's a sleeve gastrectomy, shaving off part of the stomach and so you have 7:24 less space 7:25 for food. 7:26 There's the ruined wire gastric bypass which looks complicated but really the 7:31 take off 7:31 a message for bariatric surgery is that bariatric surgery is associated with a 7:37 reduced all cause 7:38 mortality to non-surgical management for obesity and what all cause mortality 7:45 means 7:45 is that any death that occurs in patients who have obesity regardless of the 7:51 cause of 7:51 the death. 7:54 So I hope you enjoyed this video. 7:56 You talked about obesity, how to measure weight using BMI or waist 8:02 circumference, the different 8:03 causes and risk factors for obesity as well as the complications and treatment. 8:07 Thank you for watching and I hope you enjoyed this video.