Gout

Gout is a common inflammatory arthritis that is increasing in prevalence. Gout (monosodium urate crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate saturation. Tends to occur earlier in life in men than women, and is rare in childhood. Prevalence is increasing. It is associated with many serious comorbidities such as hypertension, chronic kidney disease, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Gout: Defective metabolism of uric acid can build up in joints causing arthritis, especially in the smaller bones of the feet, deposition of chalk-stones, and episodes of acute pain.
Pseudogout: Deposits of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the fluid and tissues of the joints, leading to intermittent attacks of arthritis.
Tophi: Firm, painless deposits of urate crystals in soft tissues, seen in chronic gout. Common sites include fingers, toes, elbows, and ears. They may ulcerate or deform joints and indicate long-standing uncontrolled hyperuricaemia.
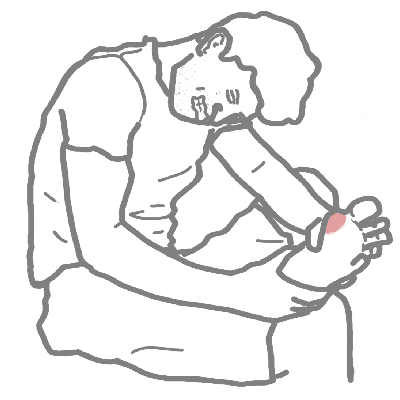
Podagra: Classic first presentation of gout in the first MTP joint
Hyperuricaemia results from either overproduction or, more commonly, underexcretion of urate. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (e.g. allopurinol) reduce uric acid production
There is a causal relationship between hyperuricaemia (high urate level) and gout.
| Risk Factors |
| Older age |
| Male sex |
| Consumption of meat, seafood, alcohol |
| Menopausal status |
| Medications (Diuretics, cyclosporine/tacrolimus, pyrazinamide, aspirin) |
| Genetics |
| Haematological Malignancies (High cell turn over) |
| Chemotherapy (High cell turn over) |
| Diabetes |
Crystal phagocytosis is central to triggering acute inflammation
Three classic stages in the natural history of progressive urate crystal deposition disease (gout):
Gout does not occur only in the great toe (podagra), although this is a common site for the initial episode.
1. Acute gouty arthritis
2. Intercritical gout
3. Chronic articular and tophaceous gout
| Monoarthropathy | Oligoarthropathy | Polyarthropathy |
| Septic arthritis | Crystal arthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Crystal arthritis (Gout or Pseudogout) | Psoriatic arthritis | Viral Arthritis |
| Osteoarthritis (can be mono-poly) | Reactive arthritis | Autoimmune connective tissue disease (ie. SLE) |
| Trauma (Haemarthrosis) | Ankylosing spondylititis | Vasculitides (ie. Polymyalgia Rheumatica) |
The chance of developing gout increases with increasing serum concentrations of uric acid.
With any monoarthritic presentation, septic arthritis should be ruled out. This can be done with a Joint aspirate.
| Synovial fluid analysis | |||
| Aetiology | Colour and Clarity | WBC (mm³) | |
| Normal | Normal | Clear and transparent | <200 |
| Non-Inflammatory | Osteoarthritis | Yellow and transparent | 0 to 2000 |
| Inflammatory | Gout | Yellow and traslucent-opaque | 2000-100,000 |
| Septic | Bacteria | Yellow/green and opaque | >25,000 – >100,000 |
| Haemorrhage | Trauma | Red and Bloody | 200-2000 |
Diagnosis For a definitive diagnosis of gout, urate crystals must be demonstrated in synovial fluid or in the tophus
Acute Attacks
Urate-lowering therapy (long-term):
Management plan
Allopurinol should not be stopped during acute flares of gout. Stopping allopurinol during an acute flare means therapeutic effect is lost and the urate level will rise. Historically, there has been concern that starting urate-lowering therapy such as allopurinol could worsen or prolong the acute gout flare, now this is not the case.
Allopurinol inhibits the enzyme xanthine oxidase, blocking the conversion of the oxypurines hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid. Side effects: mild to severe rash.
Colchicine inhibits microtubule assembly in leukocytes by binding tubulin, reducing chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and release of inflammatory mediators during urate crystal ingestion. It has no analgesic or urate-lowering effect. Side effects: Diarrhoea (usually dose dependent), GI upset, myopathy and cytopaenias in rare cases.

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion