Renal Cell Carcinoma
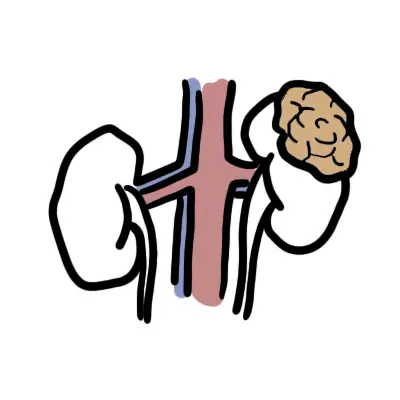

Renal cell carcinomas (originate within the renal cortex) are responsible for 85% of all primary renal neoplasms. Transitional cell carcinomas of the renal pelvis are the next most common (~8%). Renal medullary carcinoma is a rare form of RCC seen in sickle cell disease. The most common pathological type of renal cell carcinoma is clear cell carcinoma.
Von Hippel–Lindau disease: Autosomal dominant disorder, bilateral renal cell carcinomas are common and haemangioblastomas, phaeochromocytomas and renal cysts are also found
Renal cell carcinomas (RCC): arise from proximal tubular epithelium. They are the most common renal tumour in adults. They rarely present before the age of 40 years, the average age of presentation being 55 years.
Nephroblastoma (Wilms’ tumor) is common in children and make a majority of childhood primary renal carcinomas.
Renal cell carcinoma can be pathologically classed:
Clear cell carcinoma strongly asscoiated with Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) syndrome.
Kidneys are bean shaped organs that sits retroperitoneally at vertebral levels T11-L3. Above each kidney are the adrenal glands. The kidney is surrounded by a renal capsule. Surrounding the kidney + adrenal glands is the renal fascia also known as the Gerota’s fascia.
Gerota’s Fascia (renal fascia) surrounds the kidney + adrenal glands and extends to the renal vein and renal artery and wraps around the inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta.
The kidneys is divided into three sections:
Arterial Supply
Venous Drainage
Nephrons
The collecting ducts then drain into the Minor calyx → Major calyx → Renal pelvis → Ureter → Urinary bladder.
Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) syndrome ~30% of VHL patients develop RCC. estimated 60% to 70% of patients with sporadic clear cell RCC also have VHL mutations. in VHL there is anactivation of one VHL allele (found on chromosome 3p); a second loss-of-function mutation is an early initiating event for VHL cancers such as RCC.
| Risk Factors |
| Age >40 years old |
| Hypertension |
| Obesity |
| Polycystic Kidney Disease |
| Smoking |
| Chronic analgesic use |
| Sickle cell disease |
| Renal stones |
| Chronic hepatitis C infection |
| Aromatic amines |
| Cyclophosphamide |
| Schistosoma haemotabium (squamous cell carcinoma) |
| Chronic irritation (squamous cell carcinoma) |
| Aristolochic acid |
Asymptomatic until the disease is advanced
Symptomatic
Haematuria with blood clots are almost always due to nonglomerular bleeding.
Up to 20% to 30% of RCCs present with paraneoplastic syndromes.
Surgery treatment
Medical treatment Used for metastatic disease
Chemotherapy is rarely used as tumours are not chemosenstitive.
Periodic radiological follow-up is recommended in most cases so that locally recurrent or metastatic disease can be detected at an early stage.

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion