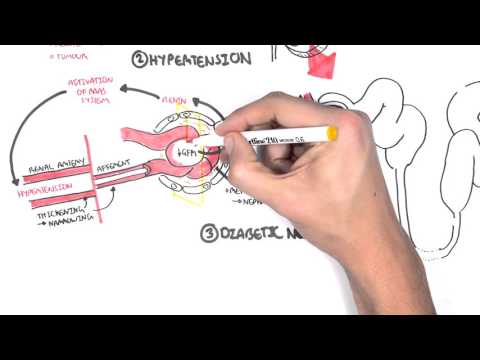
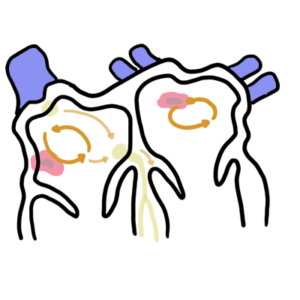
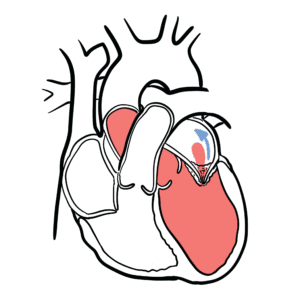
0:00 Hello, in this video we're going to talk about hypertension or high blood 0:07 pressure. 0:08 This is an overview and introduction. 0:12 Hypertension is divine its blood pressure of 140 over 90 millimeters mercury or 0:17 greater. 0:18 The main goal of treatment is to decrease the risk of mortality and of 0:22 cardiovascular 0:23 and renal morbidity. 0:26 The signs and symptoms of hypertension include headache, dyspnea, high blood 0:32 pressure, possible 0:33 retinopathy and visual changes, chest pain and sensory or motor problems. 0:42 There can also be signs of end organ damage due to hypertension if the 0:47 hypertension 0:48 is untreated and severe. 0:52 We will talk about end organ damage towards the end of the video. 0:58 So what is blood pressure? 1:02 Well it is the product of cardiac output and the total peripheral vascular 1:07 resistance. 1:08 So here is a hot pumping blood out. 1:11 This is the cardiac output and together with the total peripheral resistance 1:17 makes up the 1:18 average blood pressure. 1:23 Risk factors for hypertension are obesity, high alcohol intake, metabolic 1:30 syndrome, diabetes, 1:32 high sodium intake, sleep apnea, dyslipidemia, old age and family history. 1:44 Hypertension can be a disease in itself or it can be secondary to another 1:48 condition, 1:49 an underlying disease. 1:51 Let us look at the differential diagnoses. 1:56 Hypertension can be categorized as primary, also known as essential 2:00 hypertension or secondary 2:01 hypertension which is hypertension as a result of an underlying often 2:06 reversible cause. 2:10 Primary hypertension is basically genetics and lifestyle. 2:15 Secondary causes of hypertension include coactation of the aorta, phyochromocyt 2:21 oma, hyper-eldosteroneism, 2:23 cushing syndrome, renal artery stenosis, chronic kidney disease, polycystic 2:30 kidney disease, 2:31 nephritic and nephrotic syndrome, obstructive uropathy, hyperthyroidism and 2:38 hyperparathyroidism. 2:41 It is also sleep apnea, chronic alcohol use, use of oral contraceptives, non- 2:48 steroidal 2:49 anti-inflammatory drugs, illicit drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamine, and 2:55 preeclampsia 2:56 in females. 2:58 So those again were some causes of secondary hypertension. 3:04 The pathological vascular changes that occur in hypertension occur slowly. 3:10 Normal vessels have good blood flow, however in hypertension and as 3:16 hypertension progresses 3:18 there is vascular changes, remodeling and hypertrophy. 3:24 In the early stages you begin to have plaque buildup and thickening of the 3:31 vessel wall 3:32 and in the late stage you get even more plaque buildup due to the dysfunction 3:37 of the endothelial 3:38 vascular wall and you also get hypertrophy. 3:44 All these changes result in narrowing of the lumen and buildup in vascular 3:48 pressure resulting 3:49 in or aggravating hypertension. 3:54 These vascular changes can eventually result in end organ damage which includes 4:00 stroke, 4:01 retinopathy, transient ischemic attack, left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiac 4:08 failure and 4:09 renal failure. 4:13 Some investigations that should be performed in a patient with hypertension 4:19 include ECG 4:20 or electrocardiogram to check for cardiac function, urinalysis for renal 4:27 function and 4:27 serology tests such as plasma renin, plasma aldosterone, the thyroid function 4:32 test and 4:33 for blood count to relax other differentials and to monitor hypertension. 4:40 Management of hypertension include exercise, reducing salt intake, being on a 4:45 proper diet, 4:47 alcohol intake, smoking cessation and use of anti-hypertensives such as ACE 4:53 inhibitors.