Notes »
disease
» Intensive Care Unit
Cardiac Arrest
Overview
Overview Cardiac arrest is a state of circulatory failure due to a loss of cardiac systolic function. It is the result of 4 specific cardiac rhythm disturbances:
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
- Pulseless Electrical activity
- Asystole
Epidemiology
- Survival is estimated at <20% for patients presenting out-of-hospital with VF, and <10% overall for patients presenting with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
- 36% of patients with VF/ VT & 11% of patients with PEA/asystole, presenting in-hospital, survive to discharge.
Initial Assessment and Management
| PRIMARY SURVEY | ||
| Assessment | Management | |
| Airway | Patency | |
| Look - swelling, injury or object around mouth/face | Jaw thrust, chin lift, positioning, clear debrisGuedel, nasopharyngeal airway, LMA | |
| Listen - speech, stridor, gurgling | ||
| Feel - facial fractures | ||
| Protection | ||
| AVPU or GCS | Intubate GCS <8 → cricothyroidectomy if unsuccessful | |
| Breathing | Look, listen, feel | |
| Effort - Respiratory rate, accessory muscle use, chest wall movement | High flow 100% oxygen. Commence CPR if unresponsive or not breathing | |
| Efficiency - SaO2, cyanosis, paradoxical breathing | +/- ABG | |
| Injury - tracheal position, flail chest, chest injury | Treat pneumothorax of injury. Chest X-ray | |
| Circulation | HR, BP, capillary refill | IV access 2 large bore cannula - Fluid resus |
| Heart sounds | ||
| ECG | Arrhythmia - Defib | |
| Disability | GCS/AVPU | Maintain cerebral perfusion - O2, ventilation and circulation (above) |
| Blood sugar level | Hypoglycaemia- IV dextrose OR Hyperglycaemia - Insulin | |
| Pupils - reactive and equal | ||
| Neurological assessment | ||
| Exposure | Temperature | Maintain normothermia - blankets, +/-heaters |
| Assess other part of body including back | Manage injuries | |
Advanced Life Support
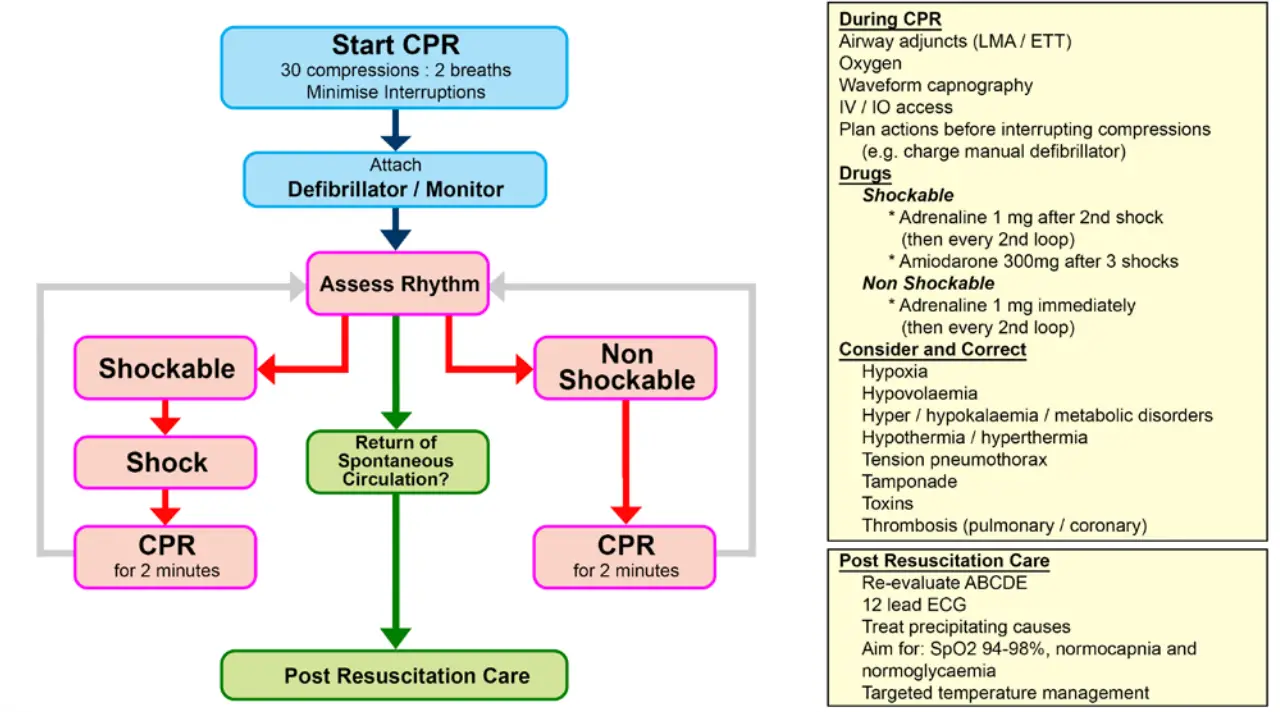
Shockable Rhythms
- Pulseless Ventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
Non-Shock
- PEA
- Asystole
Defibrillation is a process used to stop irregular crazy heartbeats by sending an electric shock in an attempt to revert the heart back to normal rhythm.
Process for using a defibrillator- COACHED
- Compression continued
- Oxygen away
- All else clear
- Charging
- Hands off/Im safe
- Evaluate rhythm
- Defibrillation or disarm and dump
Reversible causes of Cardiac Arrest
Causes 4 H's & 4 T's
- Hypoxia
- Hypovolaemia
- Hyper/Hypokalaemia
- Hyper/Hypothermia
- Tension pneumothorax
- Tamponade
- Toxins
- Thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary)
| REVERSIBLE CAUSES OF CARDIAC ARREST | ||
| Cause | Assessment | Management |
| Hypoxia | SpO2 %, ABG/VBG | Airway, Breathing; Ventilatimg with high flow O2 |
| Hypovolaemia | BP, HR, identify site of fluid loss, Burns etc | IV fluids 20 ml/kg |
| Hypothermia | Shivering, core temperature | Warm the patient aggressively to achieve a core temperature > 30°C |
| Hyperkalaemia | EUC, ABG, ECG changes - peak T-waves, widened QRS | Insulin + glucose +/- calcium gluconate |
| Hypokalaemia | EUC, ABG, ECG changes - flat or inverted T-waves | Potassium infusion |
| Tamponade (cardiac) | Becks triad jugular vein distension, hypotension, muffled heart sounds | Pericardiocentesis |
| Tension pneumothorax | Unilateral chest expansion, trachea deviated away from pneumothorax, ↓breath sounds (air entry), hyper- resonant percussion note | Needle decompression with large bore cannula (2nd intercostal space, mid clavicular line) |
| Toxins | Angioedema, History!, abnormal LFTs, signs of toxicity | Antidote if exists. Supportive therapy |
| Thrombosis | Hypotensive, SOB, chest pain, collapse, recent surgical procedure (DVT risk factors) | Fibrinolytics are recommended in cases where PE is known or suspected |