Paediatric Viral Cutaneous Infection
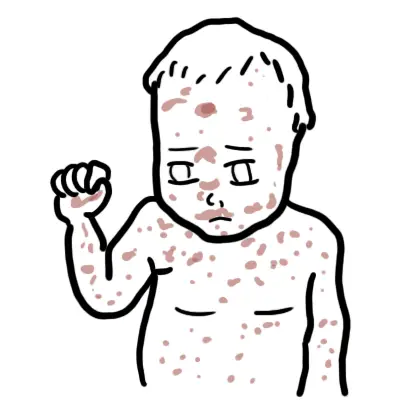

Overview
Exanthem refers to the cutaneous manifestation of a viral illness (enanthem is the manifestation in the mouth). Historically, 6 exanthems have been recognised, 4 of which are viral. However, obviously there are much more common exanthems.
The six described are:
Human herpes virus 6 and 7 also cause Pityriasis Rosea.
Overview
Also known as rubeola or first disease it is a highly contagious infection. Presents as an acute exanthematous febrile illness accompanied by conjunctivitis and koplik spots.
Triad 3 Cs for prodrome phase Cough, Coryza and Conjunctivitis then Koplik spots.


Complications common if malnourished or immunocompromised.
Overview
Generally a mild illness, but can cause devastating congenital infection. Also known as german measles or third disease. It is a minor illness in children and adults, but devastating when transmitted in utero.
Congenital rubella is still the most important cause of blindness and deafness in the neonate.
Aetiology
Clinical presentation
Hallmark of Rubella Lymphadenitis retroauricular, posterior and occipital.

Management
Congenital Rubella
Infection of the mother in the first trimester can lead to abortion or stillbirth, or to fetal malformation, including congenital heart disease, deafness and blindness (cataract or glaucoma).
Overview Also known ‘slapped cheeck’ or fifth disease.
Aetiology
Clinical presentation

Management
Complications
Papular Purpuric Gloves and Socks Syndrome is also caused by parvovirus B19 and presents with erythema, oedema, petechaie and purpura of palms and soles + burning and pruritus. It is self limiting and occurs in children and adolescents.
Overview
Also known as exanthema Subitum and sixth disease.
Aetiology – Human herpes 6 virus
Clinical presentation
| Remember |
High grade fever for 3 days (maybe URTI) which progresses to maculopapular rash all over body.

Complications
Overview
Pityriasis Rosea is a self-limiting skin rash thought to be caused by herpesvirus 6 or 7. Herald patch is often the primary lesion followed by additional similar smaller lesions around. Herald patch often misdiagnosed initially as a tinea infection.
Aetiology
Clinical Presentation

Investigation
Management
Overview
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection of childhood that causes localised clusters of epidermal pearly papules with central umbilication
Aetiology
Clinical presentation

Management
2 year old infant bought in with vesicular rash on her hand, foot and mouth.
Overview Mild vesicular eruption caused by a Coxsackie A virus.
Aetiology
A child presenting with fever and vesicles likely has chickenpox, hand foot and mouth or herpes simplex.
Clinical presentation
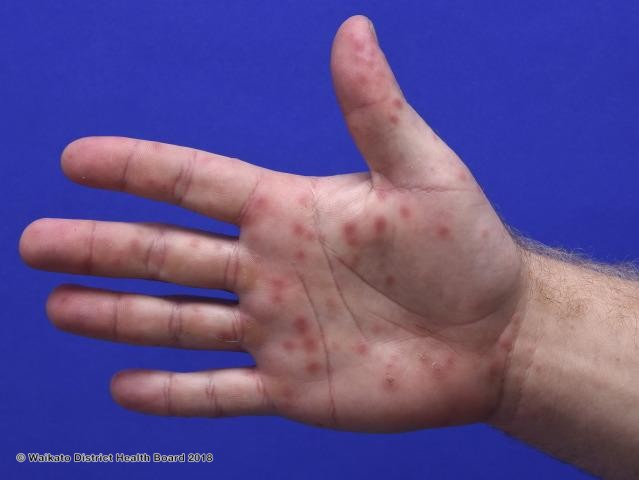
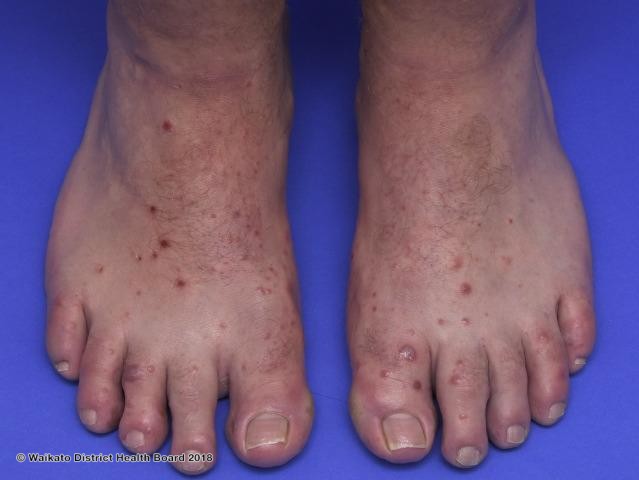
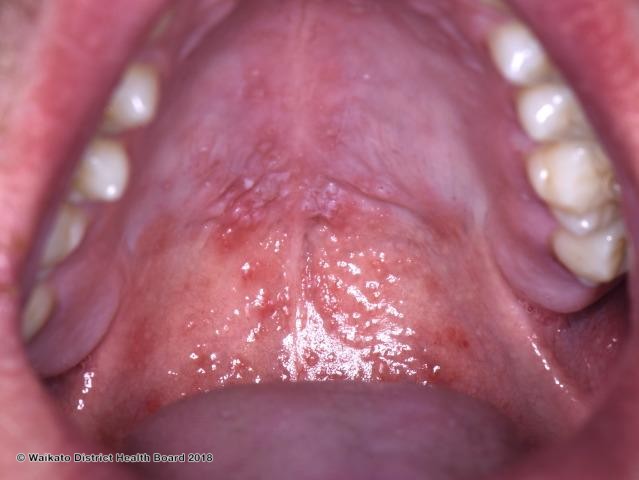
Management
Complications
A 12 year old boy present with fever sore throat and follicular conjunctivitis
Clinical Presentation
| Acute follicular conjunctivitis (usually viral) |
| Adenovirus |
| Herpes zoster virus |
| Epstein-Barr virus |
Management
Overview
Benign epidermal tumors caused by multiple types of human papillomaviruses. The common wart (verruca vulgaris) occurs particularly on hands, knees and elbow.
Aetiology
Clinical Presentation
Management depends on type and number of warts, the location on the body, and the age of the patient
Overview
Common, contagious viral infection involving the skin characterised by pruritic vesicles which eventually crust over. Clinical reactivation later in life results in herpes zoster (shingles). It is transmitted by airborne spread.
A child presenting with fever and vesicles likely has chickenpox, hand foot and mouth or herpes simplex.
Aetiology
Virus can become latent in sensory ganglia and reappears as herpes zoster (shingles) later in life.
Clinical Presentation – all stages of rash is seen
Adults can also present with chicken pox and these are often more severe.

Management
Complication
A child presenting with fever and vesicles likely has chickenpox, hand foot and mouth or herpes simplex.
Overview
Primary Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in children is usually asymptomatic or non- specific. Herpetic gingivostomatitis is the most common specific clinical manifestation, occurring in 25% to 30% of cases.
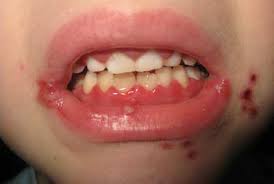
Clinical presentation
Management
Complications
Overview
Infectious mononucleosis is a febrile illness caused by the herpes (Epstein– Barr) virus. It can mimic diseases such as HIV primary infection, streptococcal tonsillitis, viral hepatitis and acute lymphatic leukaemia
Aetiology
Classification
Clinical Presentation
Infectious mononucleosis triad Sore throat, fever and lymphadenopathy.
Differential Diagnosis
Investigations
Management
Morbilliform eruption may occur after treatment with ampicillin.
Complications
Advise against alcohol, fatty foods, continued activity, especially contact sports (risk of splenic rupture).

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion