Notes »
disease
» Paediatrics
Henoch-Schönlein purpura (Spring Fever)
Overview
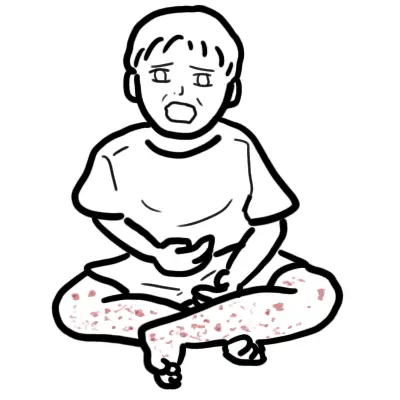
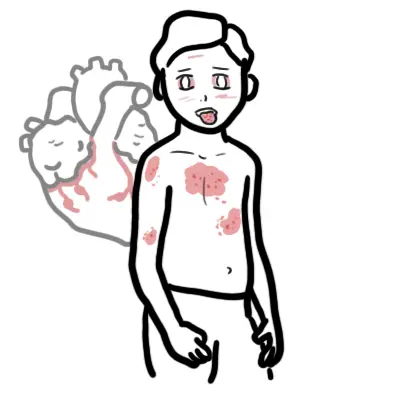
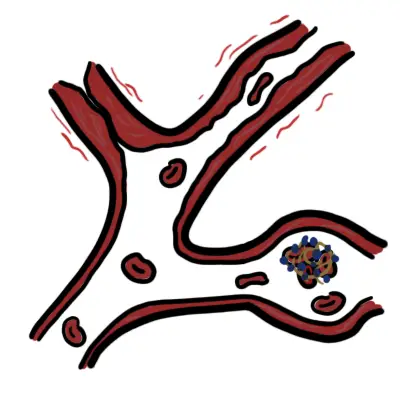
Henoch Schonlein Purpura is a IgA vasculitis characterised by the Tetrad: palpable purpuric petechial rash, abdominal pain, kidney involvement and arthralgia. Aetiology is unknown but thought to have a genetic predisposition.
Clinical Manifestation
| Henoch Schonlein Purpura Tetrad Palpable purpuric petechial rash, abdominal pain, kidney involvement and arthralgia. |
- Recent mucosal infection (respiratory or gastrointestinal)
- Rash
- Abdominal pain
- Nephritis
- Arthrlagia of large joints
- Oedema of extremities
- Hypertension (due to kidney involvement)
| Side note Kidney involvement in HSP is similar to IgA nephropathy. |
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Purpura/Petechiae in a child
- Thrombocytopaenia
- Decreased platelet production
- Infections
- Drugs and alcohol
- Aplastic anaemia
- Leukaemia
- Myelodysplastic syndrome
- Increased platelet destruction
- Immune mediated - Immune thrombocytopaenic purpuura
- Non-immune mediated - causes of microangiopathic haemolysis (TTC, HUS, DIC, pre-eclampsia, HELLP)
- Dilutional thrombocytopaenia - from massive blood transfusion
- Distributional thrombocytopaenia - caused by splenic sequestration
- Portal hypertension
- Decreased platelet production
- Non-thrombocytopaenia
- Vasculitis
- Henoch Schonlein pupura
- Wegener’s granulomatosis
- Hand, foot and mouth disease (Coxsackie virus)
- Meningococcemia
- Vasculitis
Investigation
- Urinalysis
- Haematuria
- Proteinuria
- Urine culture
- Blood culture
- FBC
- EUC
- Albumin
- Screen for nephritic differentials
- ANA
- Anti-DNA
- Anti-Smiths
- ESR/CRP
- Ultrasound
- PT/APPT - normal because it is not a clotting problem it is a vascular problem
Treatment
Acute management
- Mild pain
- Paracetamol
- NSAIDs (if not older)
- Elevate oedematous lower limb
- Moderate-severe pain
- Admit
- IV steroids OR oral steroids
- Paediatric consult
- Elevate oedematous lower limb
Ongoing management
- Regular GP/Paediatrician review for progress and complications
Complications and Prognosis
- Bowel infarction
- Bowel perforation
- Intussusception
- PR bleeding
- Respiratory disease
- Nephritic/Nephrotic syndrome
- Intracranial Haemorrhage