Overview
Junctional rhythms occur when the AV node takes over as the primary pacemaker. Junctional rhythm usually is associated with a benign course.
Mechanism
- SA node has failed
- AV node just wants to be faster and takes over
- Enhanced automaticity in AV nodal cells
Think
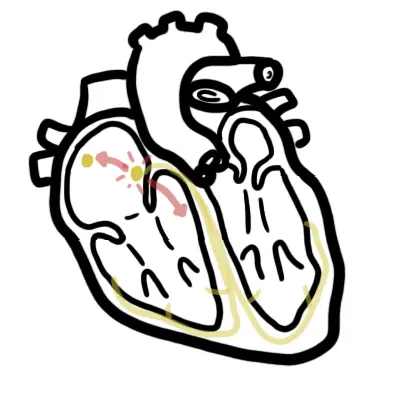
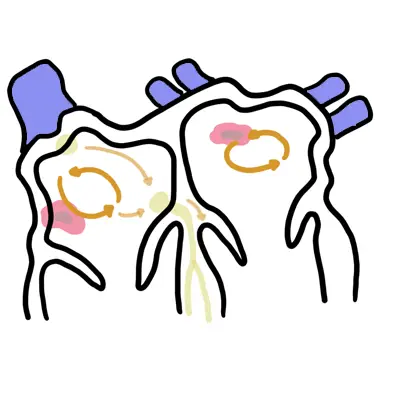
AVNRT – Seperate condition where a re-entry loop stimulates the AV node again and again.
Aetiology and Risk Factors
Aetiology
- Digoxin – classic cause
- Beta-agonists, e.g. isoprenaline, adrenaline
- Myocardial ischaemia
- Myocarditis
- Cardiac surgery
- Hypokalaemia
- Cardiac surgery
Junctional rhythm ECG features
- Narrow QRS (<1.2)
- Ventricular rate 60-100
- Shortened PR interval
- Inverted P wave just before QRS
- P wave buried in QRS
Remember
Junctional tachycardia has narrow QRS, absent or inverted P waves.
Diagnosis
- AVRT
- AVNRT
Treatment
- Usually observation
- Treat underlying cause if needed
- Discontinue causative medications
- Permanent pacemaker


Discussion