Notes »
disease
Thyroiditis
Overview
| Definition Thyroiditis: Varied group of disorder all characterized by some form of thyroid inflammation Hyperthyroidism: denote conditions in which hyperfunction of the thyroid leads to thyrotoxicosis. Hypothyroidism: Variety of abnormalities that cause insufficient secretion of thyroid hormones. The most common cause is autoimmune thyroid disease Thyrotoxicosis: denotes the clinical, physiological, and biochemical findings that result when the tissues are exposed to excess thyroid hormone. It can arise in a variety of ways. |
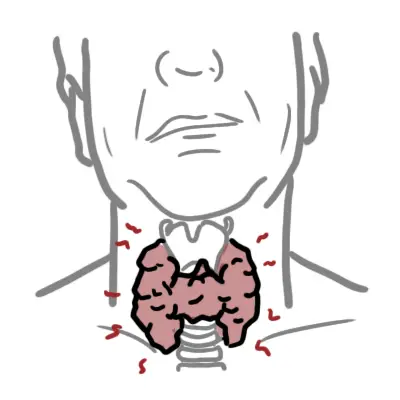
The term thyroiditis refers to a varied group of disorders all characterized by some form of thyroid inflammation. It includes conditions characterized by thyroid pain and tenderness and those with goiter without pain.Inflammation of the thyroid gland often leads to a transient thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism.
Clinical Manifestation
Acute thyroiditis
- painful
- tender thyroid
- fever
De Quervain
- Painful
- Arthralgia
- Respiratory tract infection
- Malaise
Hashimoto's (hypothryoidism)
- Painless
- Goiter
- Thyroid rubbery consistency and an irregular surface.
Riedel thyroiditis (chronic fibrosing thyroiditis)
- Hard woody consistency of thyroid
Diagnosis
| Causes and characteristics of thyroiditis | |
| Cause | Characteristic features |
| Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis | Grossly lymphocytic and fibrotic thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism |
| Postpartum thyoiditis | Lymphocytic thyroditis, transient thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism |
| Drug induced | Particularly with amiodarone |
| De Quevain | Thought to be viral in origin, multinuclear giant cells |
| Riedel thyroiditis | Extensive fibrosis of the thyroid |
| Radiation thyroiditis | Radiation injury, transient thyrotoxicosis |
Treatment
Painful Thyroiditis
- Aspirin
- Steroids