Notes »
clinical
» Neurology
Parkinson's Presentation
Overview
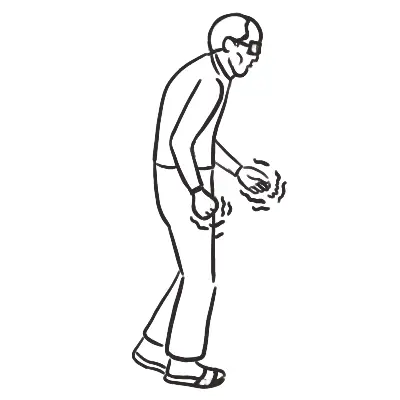
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterised by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and a wide spectrum of non-motor symptoms including sleep disorders, hyposmia, bladder and bowel dysfunction, fatigue, dementia, and other neuropsychiatric symptom. Although the disease has no cure, available treatments effectively control motor symptoms and improve quality of life. Parkinson disease affects approximately 1 percent of persons older than 60 years, and up to 4 percent of those older than 80 years.
Examination
General
- Mask-like facies
- Resting tremor
- Pill rolling
- Flexed posture
- Walking aid?
Gait
- Shuffling → Festinating → Difficulty stopping
- Heel to toe difficult
- No arm swing
Movement
- Resting tremor (make them not think about it)
- Propulsion and Retropulsion (not recommended)
- Bradykinesia
- Tapping the fingers
- Twiddling
- Opening door knob
- Kinesia Paradoxica (not recommended)
- Orthostatic hypotension
Head
- Titubation
- Dribbling
- Absence of blinking
- Glabbelar tap
- Speech - monotone, soft
- Oculomotor movement - upward gaze problems
- Supranuclearpalsy - loss of all gaze movement
- Seborrhoea - autonomic dysfunction
- Palmomental Reflex
Arms
- Hypertonia - cogwheel rigidity usually begins asymmetrically
- Micrographia
- Test higher centers of brain..
Differentials for Parkinson's Disease
- Drug induced - Antipsychotics
- Tumour
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Stroke
- Huntington's
Rule out Parkinson Plus syndrome
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Multi-system atrophy
- Parkinsonism-dementia-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis complex
- Corticobasal ganglionic degeneration (CBD)
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Mini-mental state examination to distinguish from pure parkinson's disease
| More information of Parkinson Plus Syndrome click here |
| Classification of Tremor | |
| Resting Tremor | Parkinson's |
| Postural/action tremor | Idiopathic, anxiety, drugs, familial |
| Essential Tremor | Familial |
| Intention tremor | Cerebellar (increases towards target) |
| Midbrain tremor | Movement of upper limbs associated with intention tremor |