Overview
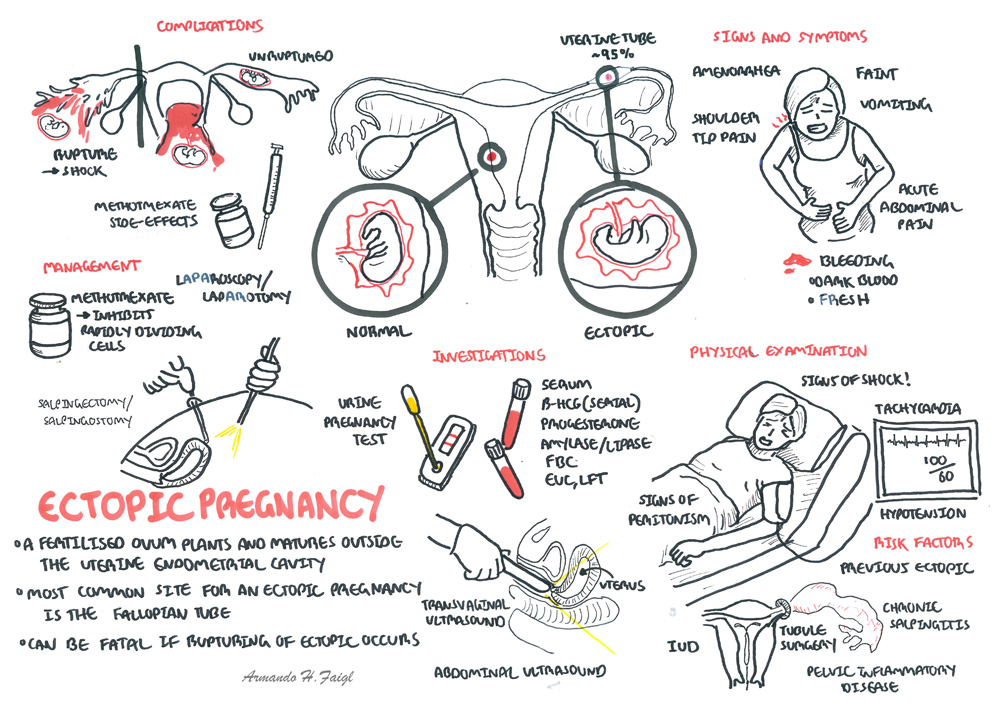
| Definition Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy in which the fetus develops outside the womb, typically in a fallopian tube Amenorrhoea: Absence of mentruation Laproscopy: A surgical procedure in which a fibre-optic instrument is inserted through the abdominal wall to view the organs in the abdomen or permit small-scale surgery Laparotomy: A surgical incision into the abdominal cavity, for diagnosis or in preparation for major surgery Salpingectomy: Surgical removal of the fallopian tubes Salpingostomy: Creation of an opening into the fallopian tube, but the tube itself is not removed in this procedure |
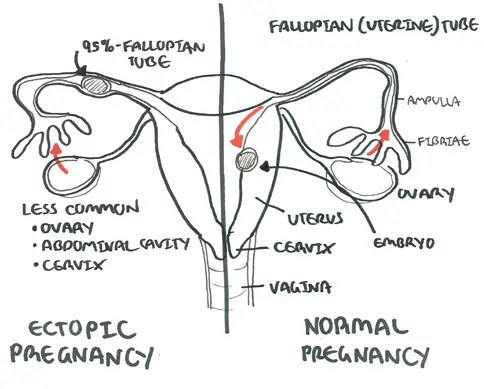
| Remember The most common site for ectopic pregnancies is a fallopian tube. |
| Watch Video: Ectopic Pregnancy Overview |
Anatomy and Physiology
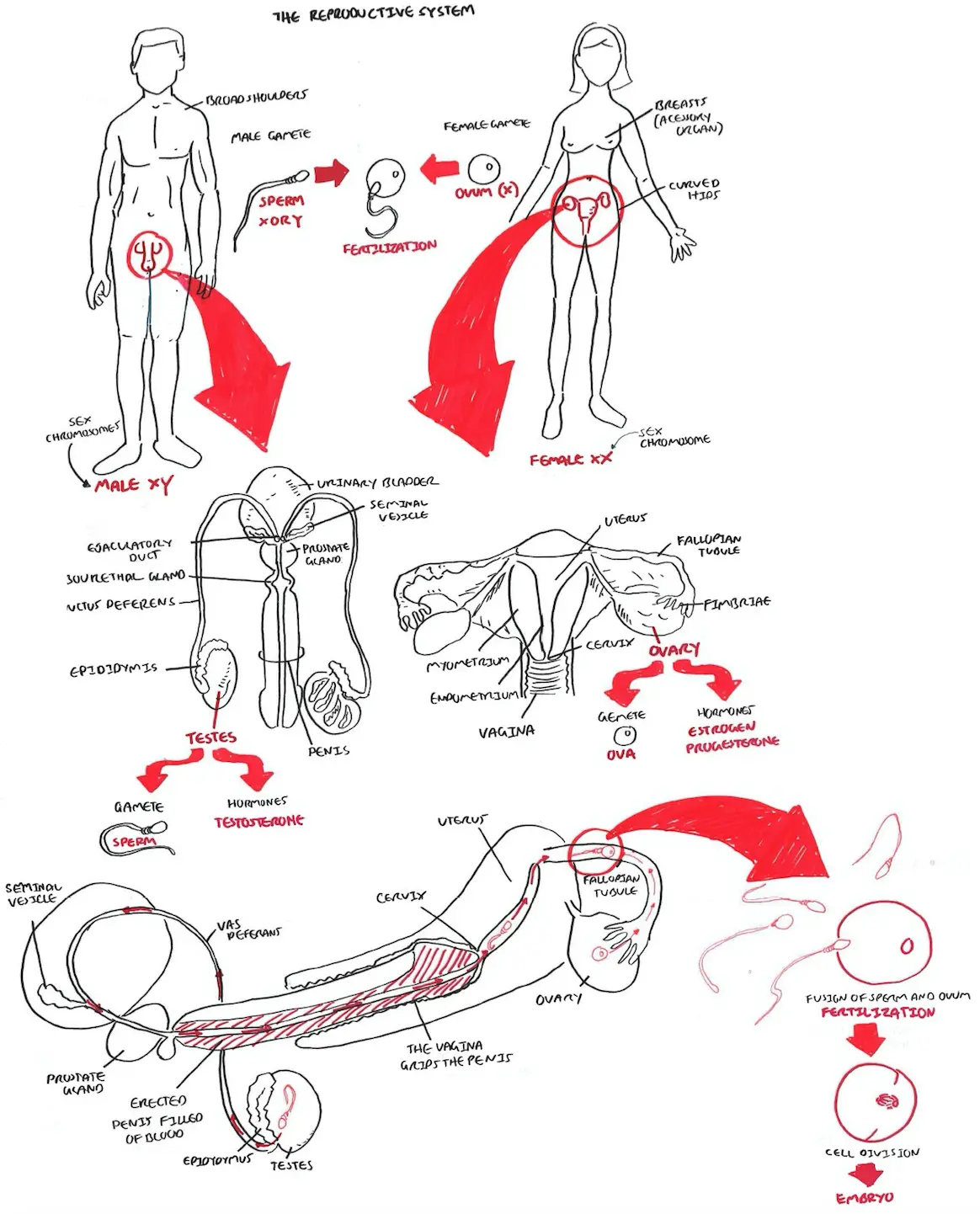
Risk Factors
More than half of patients with ectopic pregnancy have no risk factors.
| Risk Factors | |
| High | Previous ectopic Previous tubal surgery Tubal pathology In utero DES exposure Current IUD use |
| Moderate | Infertility Previous cervicitis History of PID Multiple sexual partners Smoking |
| Low | Previous pelvic/abdominal surgery Vaginal douching Early age of intercourse |
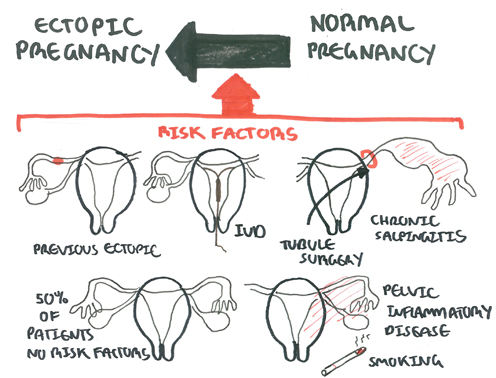
| Remember Although pregnancy is unusual after tubal ligation, when it does occur there is a relatively high chance (1 in 6) of it being an ectopic pregnancy |
Signs and Symptoms
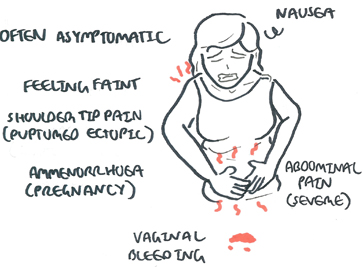
Clinical Presentation differs if the patient has an ectopic or an ruptured ectopic.
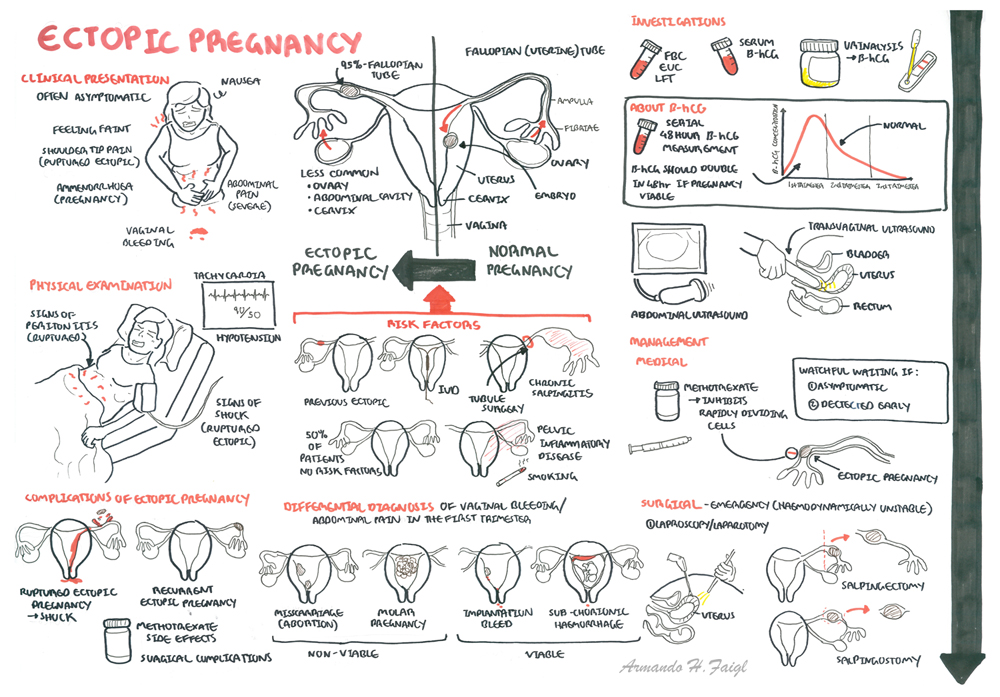
- Ectopic Pregnancy is often asymptomatic.
- Amenorrhea because of pregnancy
- Pelvic pain and tenderness (palpation and bimanual examination).
- Vaginal bleeding
- Faint and nauseous.
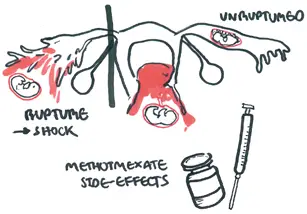
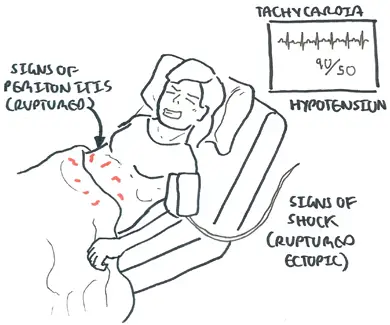
If rupture of ectopic occurs, there is blood, acute abdomen with increasing pain (+/- shoulder tip pain), abdominal distention and signs of shock.
| Ectopic Pregnancy Triad: amenorrhea, vaginal spotting, and abdominal pain. |
| Remember Rule out ectopic pregnancy in a female patient in reproductive age who presents with an acute abdomen regardless of history and examination findings. |
Examination
Differential Diagnosis
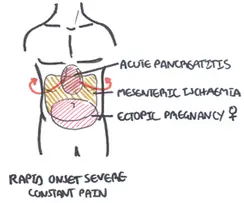
Differential Diagnosis for ectopic pregnancy
- Acute salpingitis
- Abortion
- Ruptured corpus luteum
- Acute appendicitis
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Adnexal torsion
- Degenerating leiomyomata
- Endometriosis
Investigation
For any pregnant lady presenting with abdominal pain and/or vaginal bleeding the most important investigations:
- FBC
- EUC
- Urine analysis
- β-hCG - Pregnancy test is almost always +ve, but serum B-HCG levels are lower than expected for normal pregnancy
- Ultrasound
Other Investigations to support or rule out differentials
- Progesterone
- Amylase/Lipase
- LFT
- ESR/CRP
| Remember Levels of hCG that plateau in the first 8 weeks of pregnancy indicate an abnormal pregnancy, which may either be a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. |
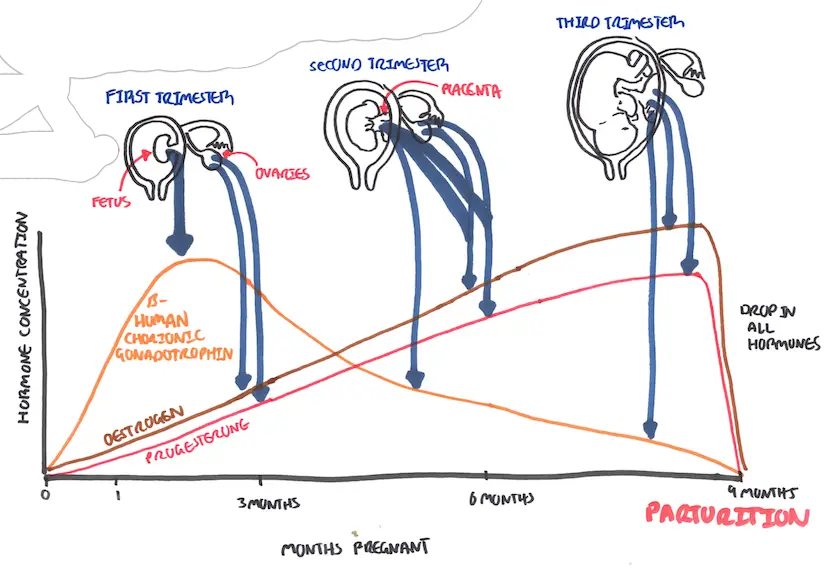
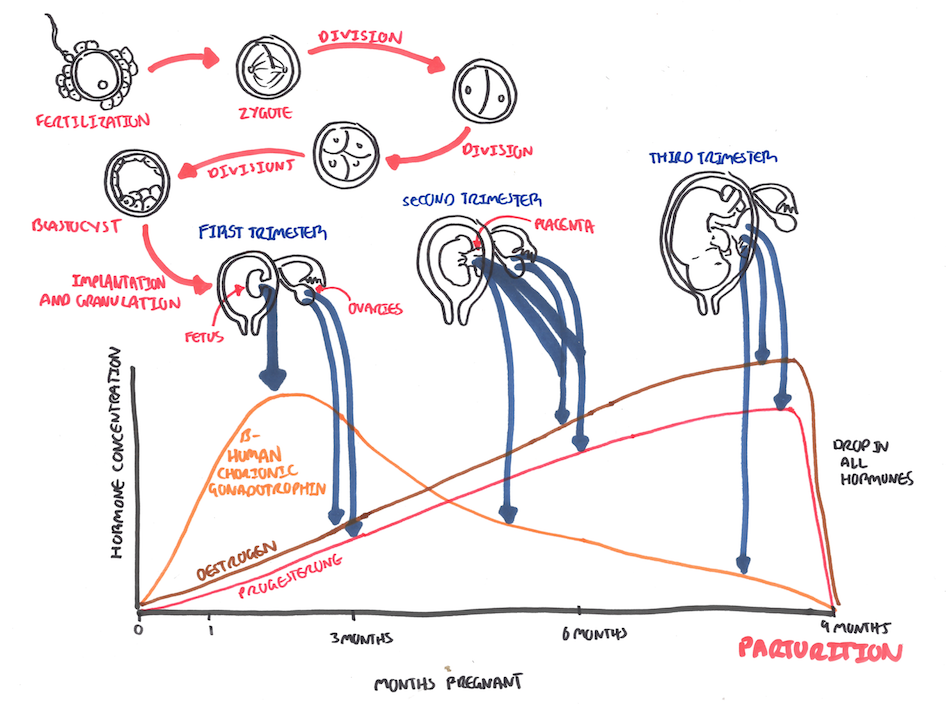
Hormonal changes in pregnancy. Note First trimester bHCG peaks then drops steadily.
When the hCG level equals or exceeds 1500 to 2000 mIU/mL, an intrauterine gestational sac is usually seen on transvaginal ultrasound; in fact, when the hCG level meets or exceeds this threshold and no gestational sac is seen, the patient has a highikelihood of an ectopic pregnancy
| B-HCG levels and correlation | |
| b-HCG rising normally | |
| b-HCG rising but not normally | |
| b-HCG is decreasing | failed pregnancy (eg, spontaneous abortion, tubal abortion, spontaneously resolving ectopic pregnancy). |
Management
Management option depends on clinical presentation and setting. Emergency setting where the patient is haemodynamically unstable will be discussed in the next section.
- Watch and wait for resolution - if detected early and not symptomatic
- Medical treatment using Methotrexate - if β-hCG not going down
- Surgery - is symptomatic
- Laproscopy (Key hole surgery) +/- salpingectomy or salpingostomy
- Laparotomy (Open surgery) +/- salpingectomy or salpingostomy
| Remember Salpingectomy is removal of the fallopian tube (uterine tube). Salpingostomy is removing a section of the fallopian tube (uterine tube) |
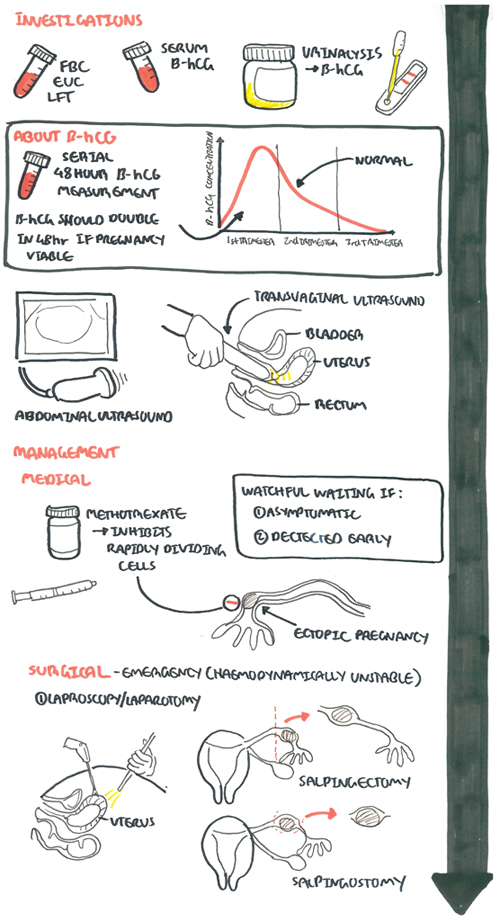
| Indications for salphingectomy |
| Recurring ectopic pregnancies or are > 5 cm |
| Severely damage tubes |
| No future childbearing is planned |
Methotrexate therapy The optimal candidates for MTX treatment of ectopic pregnancy are hemodynamically stable, willing and able to comply with post-treatment follow-up, have a human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentration ≤5000/mL, and no fetal cardiac activity.
Contraindications for ectopic include renal failure, immunodeficiency, allergy, heterotopic pregnancy with coexisting viable intrauterine pregnancy, breastfeeding, unable to complete methotrexate management
| Pharmacology Methotrexate is a folic acid antagonist widely used for treatment of neoplasia, severe psoriasis and Rheumatoid arthritis. Side effects of methotrexate is conjunctivitis and gastrointestinal upset. |
Emergency
Haemodynamically unstable patients (ruptured ectopic)
Signs and symptoms
- Acute abdomen with worsening pain
- Abdominal distention
- Shoulder tip pain (kehr's sign)
- Signs of shock
Management
Resuscitation
- Two large-bore IV line and IV fluids
- Cross match 6U blood
- Call senior help and aesthetics assistance urgently
Surgery
- Laparotomy with salpingectomy
Complication and Prognosis
Overview
| Definition Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy in which the fetus develops outside the womb, typically in a fallopian tube Amenorrhoea: Absence of mentruation Laproscopy: A surgical procedure in which a fibre-optic instrument is inserted through the abdominal wall to view the organs in the abdomen or permit small-scale surgery Laparotomy: A surgical incision into the abdominal cavity, for diagnosis or in preparation for major surgery Salpingectomy: Surgical removal of the fallopian tubes Salpingostomy: Creation of an opening into the fallopian tube, but the tube itself is not removed in this procedure |

An ectopic pregnancy is an extrauterine pregnancy. Almost all ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube (>95%).
| Remember The most common site for ectopic pregnancies is a fallopian tube. |
| Video: Ectopic Pregnancy Overview |
| Watch Video: Ectopic Pregnancy DETAILED - Overview |
Anatomy and Physiology

Reproductive System Overview
| Watch Reproductive System Overview |

Hormones in Pregnancy
| Watch Parturition Pregnancy, Hormones |
Risk Factors
More than half of patients with ectopic pregnancy have no risk factors.
| Risk Factors |
High
|
Moderate
|
Low
|

| Remember Although pregnancy is unusual after tubal ligation, when it does occur there is a relatively high chance (1 in 6) of it being an ectopic pregnancy |
Signs and Symptoms
Clinical Presentation differs if the patient has an ectopic or an ruptured ectopic.
- Ectopic Pregnancy is often asymptomatic.
- Amenorrhea because of pregnancy
- Pelvic pain and tenderness (palpation and bimanual examination).
- Vaginal bleeding
- Faint and nauseous.
If rupture of ectopic occurs, there is blood, acute abdomen with increasing pain (+/- shoulder tip pain), abdominal distention and signs of shock.
| Ectopic Pregnancy Triad: amenorrhea, vaginal spotting, and abdominal pain. |

| Remember Rule out ectopic pregnancy in a female patient in reproductive age who presents with an acute abdomen regardless of history and examination findings. |
Examination

Pain is the most common complaint +/- vaginal bleeding. A ruptured atopic will present with signs of shock and signs of peritonism.
Differential Diagnosis

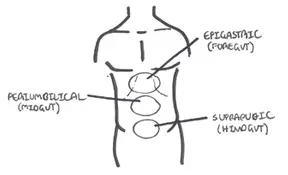
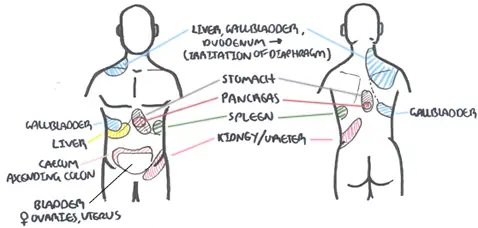
Pain can be divided as being epigastric, umbilical or suprapubic (hypogastric). Ectopic typically presents as suprapubic pain but may radiate to other areas, especially if ruptured.

Referred pain is important to understand. Certain areas of the abdomen can refer pain else where. A good example is in ectopic pregnancy when irritation of the diaphragm can cause shoulder tip pain.
Differential Diagnosis for ectopic pregnancy
- Acute salpingitis
- Abortion
- Ruptured corpus luteum
- Acute appendicitis
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Adnexal torsion
- Degenerating leiomyomata
- Endometriosis
Investigation
For any pregnant lady presenting with abdominal pain and/or vaginal bleeding the most important investigations:
- FBC
- EUC
- Urine analysis
- β-hCG - Pregnancy test is almost always +ve, but serum B-HCG levels are lower than expected for normal pregnancy
- Ultrasound
Other Investigations to support or rule out differentials
- Progesterone
- Amylase/Lipase
- LFT
- ESR/CRP
| Remember Levels of hCG that plateau in the first 8 weeks of pregnancy indicate an abnormal pregnancy, which may either be a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. |

Hormonal changes in pregnancy. Note First trimester bHCG peaks then drops steadily.
When the hCG level equals or exceeds 1500 to 2000 mIU/mL, an intrauterine gestational sac is usually seen on transvaginal ultrasound; in fact, when the hCG level meets or exceeds this threshold and no gestational sac is seen, the patient has a highikelihood of an ectopic pregnancy
| B-HCG levels and correlation | |
| b-HCG rising normally | |
| b-HCG rising but not normally | |
| b-HCG is decreasing | failed pregnancy (eg, spontaneous abortion, tubal abortion, spontaneously resolving ectopic pregnancy). |
Management
Management option depends on clinical presentation and setting. Emergency setting where the patient is haemodynamically unstable will be discussed in the next section.
- Watch and wait for resolution - if detected early and not symptomatic
- Medical treatment using Methotrexate - if β-hCG not going down
- Surgery - is symptomatic
- Laproscopy (Key hole surgery) +/- salpingectomy or salpingostomy
- Laparotomy (Open surgery) +/- salpingectomy or salpingostomy
| Remember Salpingectomy is removal of the fallopian tube (uterine tube). Salpingostomy is removing a section of the fallopian tube (uterine tube) |

| Indications for salphingectomy |
| Recurring ectopic pregnancies or are > 5 cm |
| Severely damage tubes |
| No future childbearing is planned |
Methotrexate therapy The optimal candidates for MTX treatment of ectopic pregnancy are hemodynamically stable, willing and able to comply with post-treatment follow-up, have a human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentration ≤5000/mL, and no fetal cardiac activity.
Contraindications for ectopic include renal failure, immunodeficiency, allergy, heterotopic pregnancy with coexisting viable intrauterine pregnancy, breastfeeding, unable to complete methotrexate management
| Pharmacology Methotrexate is a folic acid antagonist widely used for treatment of neoplasia, severe psoriasis and Rheumatoid arthritis. Side effects of methotrexate is conjunctivitis and gastrointestinal upset. |
Emergency
Haemodynamically unstable patients (ruptured ectopic)
Signs and symptoms
- Acute abdomen with worsening pain
- Abdominal distention
- Shoulder tip pain (kehr's sign)
- Signs of shock
Management
Resuscitation
- Two large-bore IV line and IV fluids
- Cross match 6U blood
- Call senior help and aesthetics assistance urgently
Surgery - Laparotomy with salpingectomy