Overview
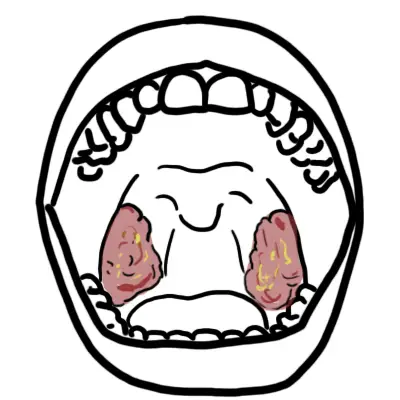
Overview Tonsillitis is inflammation or infection of the tonsils. Tonsils are lymphoid tissues that are situated on both side of the throat. Generally, the palatine tonsil are referred to as "the tonsils".
| Definition Tonsils: Collections of lymphoid tissue at the entrance to the pharynx, on either side of the uvula (the palatine tonsils). There are also lingual tonsils at the base of the tongue. All of these as well as the adenoids are part of Waldeyer’s ring Tonsillitis: Inflammation of the tonsils. Usually refering to infection Adenoids: Collection of lymphoid tissue near the opening of the Eustachian tube |
Anatomy Nasopharynx and Oropharynx
Signs and Symptoms
- Sore throat
- Odynophagia (painful swallow)
- Fever
- Malaise
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
- Enlarged red tonsils
Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of the sore throat
- Peritonsillar abscess (Quinsy)
- Infectious mononucleosis (EBV)
- Epiglottitis
- Bacterial tracheitis
- Retropharyngeal abscess
Investigations
- FBC
- EUC
- Paul-Bunnell or monospot blood test - Mononucleosis (glandular fever)
Aetiology
A typical attack of acute tonsillitis will last from 3 to 7 days. The main organisms implicated are as follow:
- Viruses
- Pyogenic bacteria:
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Pneumococcus spp.
- Group A Haemolytic Streptococcus
Pathophysiology
Management
- Analgesia (paracetamol)
- Fluids
- Antibiotics (penicillins - first line)
- Tonsillectomy is one of the most common operations performed in both adults and children.
| Indications |
| Recurrent tonsillitis >6/year |
| Tonsillolith |
| Malignancy |
| Oropharyngeal obstruction (Sleep apnoea or swalling difficulty) |
| Abscess (Quinsy) |
Complications and Prognosis
Complications
- Peritonsillar abscess (Quinsy)
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Paraphayrngeal abscess
- Mediastinitis
- Venous thombosis
- Paraphayrngeal abscess
- Rheumatic fever
- Glomerulonephritis
- Septicaemia (very rare)
- Otitis media
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
Prognosis Most cases of acute tonsillitis resolve spontaneously with no ill-effects. However, it can be a serious disease particularly in the immuno-compromised patient
Adenoids
Overview Adenoids are a collection of lymphoid tissue. They are part of a circle of lymphoid tissue known as Waldeyer’s ring that surrounds the entrance to the pharynx and respiratory tract.
Adenoids are very small and reach maximum size at 8 years of age, and then regress. Adults have little or no adenoid tissue. In children, repeated infections cause adenoids to enlarge and obstruct the airway.
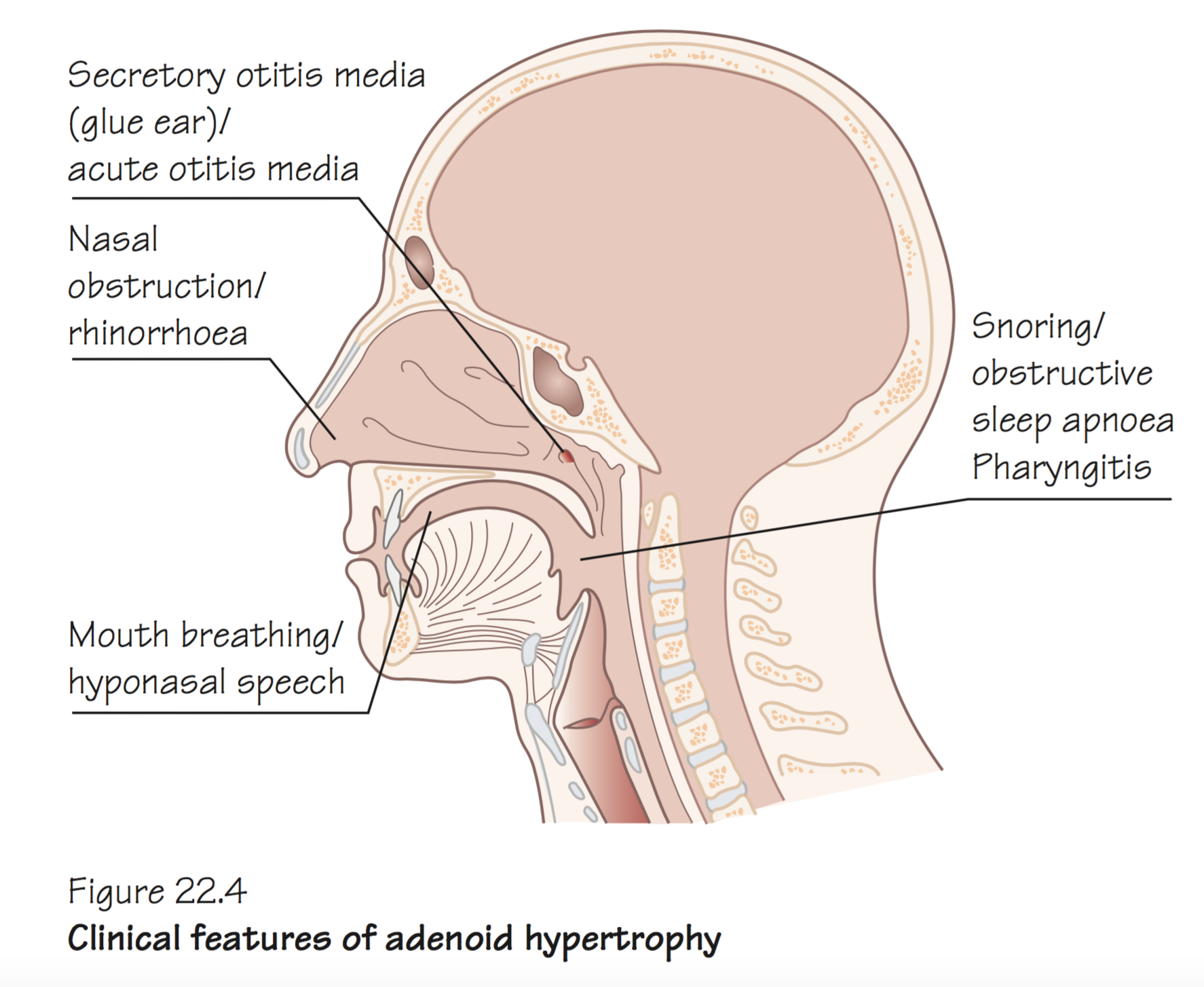
Adenoid hypertrophy Management
- Adenoidectomy (usually done with tonsillectomy)