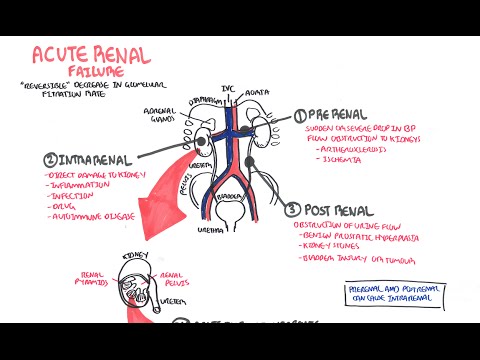
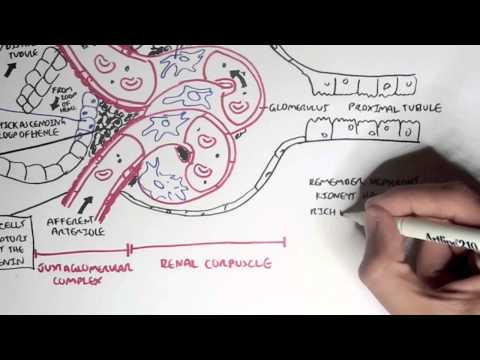
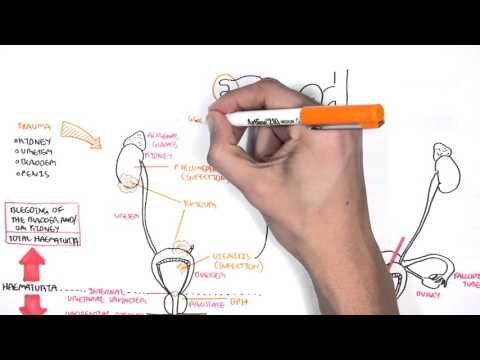
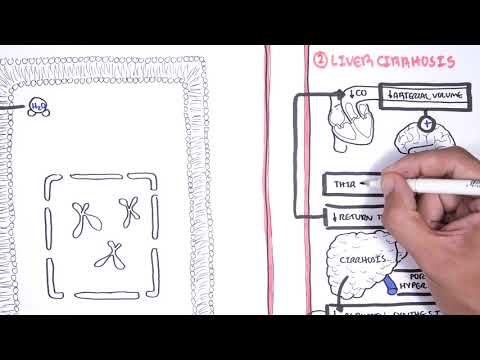
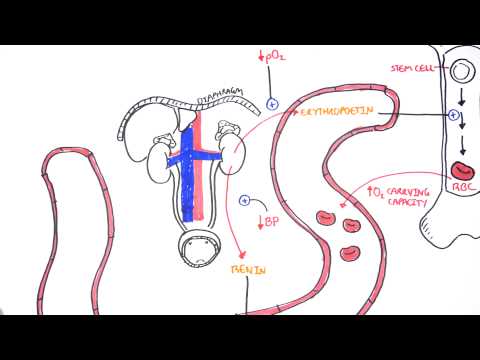
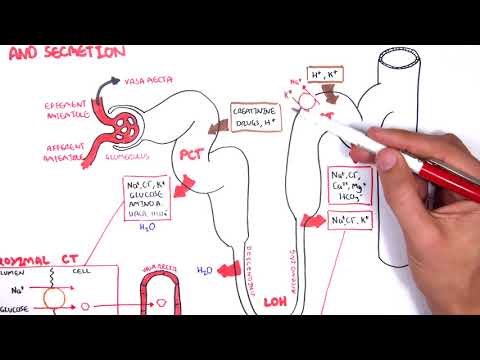
0:00 Acute kidney injury is characterized by abrupt deterioration in kidney function 0:11 and manifested 0:12 by an increase in serum creatinine level with or without reduced urine output. 0:19 So here we have the left and right kidney. 0:21 The renal artery supplies the kidneys. 0:25 The renal artery branches and supplies the functional units of the kidneys 0:28 called the 0:29 nephrons. 0:33 Now the branches of the renal arteries form what's called the glomerulus which 0:38 filters 0:38 the filtrate into the many nephron tubules. 0:46 Substances in the filtrate can be reabsorbed and many things secreted into the 0:51 tubules 0:52 along its way. 0:54 The end product is urine. 0:57 If we zoom into the area here where the glomerulus is and the tubules. 1:05 The glomerulus is where filtration occurs, the afferent arterial brings blood 1:10 into the 1:11 glomerulus, filtration occurs and then leaves via the efferent arterials. 1:18 The efferent arterial continues to form the vasorecta. 1:26 Between the tubule and the vasorecta is the interstition. 1:30 Using this diagram we can appreciate the nephrons for functions for making 1:35 urine. 1:36 The first is filtration, the glomerulus filters your blood, reabsorption and 1:42 then secretion 1:43 where the tubule returns needed substances into your blood and removes waste 1:48 along the 1:48 tubules. 1:51 And the fourth one is excretion, the final product really being urine. 1:57 Acute kidney injury is a rapid decrease in glomerular filtration that results 2:02 in abnormal 2:03 fluid and electrolyte balance and asotemia. 2:06 Asotemia being an increase in the wastes, nitrogen as well as creatinine. 2:13 Essentially, acute kidney injury can be thought of disruption in the four 2:17 functions of the 2:18 nephrons we just talked about. 2:20 Clinically, acute kidney injury is diagnosed when there is an abrupt increase 2:25 in serum 2:25 creatinine. 2:29 Creatinine comes from the metabolism of creatine in skeletal muscle and dietary 2:35 meat intake. 2:36 Creatinine is freely filtered across the glomeruli and not reabsorbed from the 2:43 tubules. 2:43 Creatinine however can be secreted into the tubules. 2:48 Thus, creatinine levels are maintained in serum. 2:54 When you have acute kidney injury, the four functions of making urine are 2:58 disrupted and 2:59 so you have an increase in the waste that is creatinine. 3:07 The main fact is affecting the actual glomerular filtration or hydrostatic 3:11 pressure which is 3:12 your blood pressure essentially and the colloid osmotic pressure and the fluid 3:16 pressure which 3:17 are going the other way. 3:20 The net filtration pressure favors going into the tubules. 3:24 In acute kidney injury, you have reduced glomerular filtration which can be due 3:30 to a number of 3:31 things. 3:32 Firstly, a reduced hydrostatic pressure which is your blood pressure or 3:36 cumulative increase 3:37 in the colloid osmotic pressure or fluid pressure from whatever cause. 3:43 As a result of these changes, you have an accumulation of creatinine in serum. 3:51 Creatinine does not get filtered by the glomerulus or secreted into the tubules 3:56 , resulting in 3:58 elevated serum creatinine. 4:02 To make it simple, the causes of acute renal injury or kidney injury can be 4:07 classified 4:07 into three types. 4:10 These are pre-renal which is as a result of decreased perfusion to the normal 4:14 kidney, 4:14 intra-renal acute kidney injury and post-renal also called post obstructive 4:20 acute kidney injury. 4:25 Pre-renal acute kidney injury is also known as pre-renal azoetemia. 4:29 Pre-renal causes include hypovolemia, reduced cardiac output like in cardi 4:36 ogenic shock, 4:37 for example, or reduced effective circulatory war volume such as in congestive 4:42 heart failure 4:43 or liver failure. 4:46 Essentially, these causes lead to reduced blood flow to the kidneys and so you 4:51 have 4:51 a reduced hydrostatic pressure, thus you get reduced glomerular filtration. 5:00 Another cause of pre-renal acute kidney injury is impaired renal auto- 5:04 regulation due to other 5:06 use of nephrotoxins such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. 5:12 Now non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, they actually cause vasoconstriction 5:17 to the 5:18 afferent arterioles and so this will result in reduced hydrostatic pressure 5:23 resulting 5:24 in reduced glomerular filtration. 5:28 Ace inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers causes vasodilation of the eff 5:34 erent arterioles 5:35 which is useful at times but in renal injury it actually amplifies the renal 5:41 injury because 5:42 it reduces the hydrostatic pressure and reduces glomerular filtration rate. 5:48 Finally, cyclosporin also causes acute kidney injury. 5:53 Now by definition the pre-renal acute kidney injury we talked about doesn't 5:58 actually involve 6:00 the parenchyma, doesn't involve the actual nephrons really. 6:05 So pre-renal acute kidney injury is usually reversible, however prolonged pre- 6:13 renal can 6:13 lead to ischemic injury causing intra-renal acute kidney injury. 6:18 And we'll talk about intra-renal acute kidney injury later. 6:21 But first let's talk about post-renal causes of acute kidney injury. 6:25 Post-renal acute kidney injury is also known as post obstructive acute kidney 6:31 injury and 6:32 it's essentially obstruction anywhere along the urinary tract from the renal 6:36 pelvis, urita, 6:38 bladder to the urethra. 6:40 It can be caused by renal stones which can cause obstruction along the urita, 6:44 this leads 6:45 to dilatation of the urita proximally termed hydronephrosis. 6:50 Other causes of post-renal include prostate enlargement, prostate cancer, 6:57 cervical cancer, 6:58 bladder cancer which causes all obstruction. 7:02 And finally here I wrote a lower urinary tract infection which is kind of 7:06 controversial 7:07 because technically it doesn't but if it goes up to your kidneys it can. 7:13 And so post-renal causes can lead to intra-renal causes of acute kidney injury 7:19 because as obstruction 7:21 or infection occurs it can be pushed up, the urine can be pushed up, the waste 7:28 pushed 7:28 up causing injury to the nephrons, increasing serum creatinine. 7:46 Interrenal causes of acute kidney injury are probably the most important to 7:50 understand 7:51 but essentially it can be divided into four types. 7:56 Interrenal causes include glomerular nephritis, tubular disease, interstitial 8:02 disease and vascular 8:03 disease. 8:07 So for glomerular nephritis it is essentially inflammation of the glomerulus. 8:11 The proper term for this is nephritic syndrome and there are many causes of it. 8:18 The second group of intra-renal causes is tubular disease. 8:23 The most important is acute tubular necrosis which is a result of prolonged is 8:28 chemia from 8:29 pre-renal acute kidney injury and is probably the most common renal injury in 8:36 hospitals. 8:38 Other tubular diseases can be from infection, injuring the tubular cells or 8:45 from nephrotoxins. 8:47 The third group of intra-renal causes are the interstitial disease. 8:54 These include acute interstitial nephritis and acute interstitial nephritis can 8:59 also be 9:00 from a number of things ischemia, infection, connective tissue diseases as well 9:06 as the use 9:07 of nephrotoxins or nephrotoxins. 9:14 The last group of intra-renal causes is vascular which includes vasculitis and 9:18 micro-angiopathic 9:20 hemolytic anemia causes such as TTP and HOS. 9:27 Now we can appreciate the pathophysiology which occurs in intra-renal acute 9:32 kidney injury by 9:34 focusing on the changes that occur in this diagram. 9:39 With prolonged pre-renal acute kidney injury or AKI for short, this can lead to 9:46 ischemia 9:46 which leads to tubular disease. 9:50 With tubular injury, the injured tubular cells form epithelial casts. 9:58 Multiple casts occurs from damaged tubules and can be seen on urine microscopy. 10:04 This will result in an inflammatory reaction whereby there is an increase in ad 10:09 hesion molecules 10:10 and leukocyte activation. 10:15 Neutrophils are recruited to the area and further perpetuate the inflammatory 10:19 response 10:19 injuring the tubules. 10:21 This causes further damage to the tubules and surrounding areas including the 10:27 interstition. 10:28 Leukocytes form white cell casts which can be seen in urine microscopy and 10:36 signifies inflammation 10:37 or infection. 10:41 Inflamed interstition from whatever cause including infection or nephrotoxins 10:45 also results in an 10:45 inflammatory response leading to leukocyte recruitment, tubular injury and 10:51 white cell 10:51 casts. 10:54 In glomerular nephritis there is inflammation of the glomerulus. 10:58 This is special because with damaged glomerulus, the red blood cells can 11:02 actually pass through 11:03 as filtrate and the red blood cells can form casts. 11:08 Again these red blood cell casts can be seen in urine microscopy and signifies 11:13 glomerular 11:14 injury. 11:16 Blomerular inflammation as well as vascular inflammation promotes the 11:20 inflammatory response 11:21 as we discussed earlier. 11:25 In intra renal aka the inflammatory response results in the release of many 11:30 peptides involved 11:32 in vasoconstriction. 11:33 This is why intra renal aka usually coexists with pre renal aka due to vasocon 11:41 striction. 11:43 When the kidneys are in this period of reduced blood flow, they are vulnerable 11:47 to further 11:48 insult with nephrotoxins such as non-stroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or amino 11:54 glycosides. 11:55 Some nephrotoxins can also directly injure the tubules or the interstition. 12:02 Important nephrotoxins to know about include non-stroidal anti-inflammatory 12:06 drugs, iodinated 12:08 are contrast, amino glycosides, myoglobin, crystals formed in your body as well 12:14 as in 12:15 myeloma where you have power proteins. 12:22 For investigations in acute kidney injury, baseline blood tests are important 12:26 and this 12:26 includes full blood count, electrolyte urea creatinine. 12:31 You will have an elevation of creatinine which is diagnostic for aka. 12:37 You may have an elevation in urea as well as nitrogen. 12:42 For pre renal, the fractional excretion of sodium and urea can be calculated 12:47 and is helpful 12:48 in diagnosing or differentiating pre renal to acute tubular necrosis for 12:54 example. 12:55 Also with pre renal, it's important to investigate or look out for the fluid 13:00 state of the patient 13:01 if they are hypovolemic or hypervolemic. 13:07 Common investigations of acute kidney injury include urinalysis, urine MCS, 13:12 microscopic 13:13 culture sensitivity, urine costs which we talked about, the different types of 13:18 costs, 13:19 renal ultrasound, urine protein creatinine ratio and albumin creatinine ratio. 13:27 For post renal causes, it's again important to do a urinalysis and urine MCS 13:33 but here 13:34 fundamentally doing a bladder scan is easy to check for essentially urine 13:38 retention. 13:39 You can check the cathode if the patient has one, see if it's blocked or kinked 13:43 because 13:43 this can cause post renal aka. 13:48 Also imaging is actually very important so CTKUB or even a renal tract 13:53 ultrasound is 13:54 useful to check for any obstruction signs. 14:01 And of AKI will depend on the cause but essentially give someone fluids if it's 14:07 a pre renal cause 14:08 and they're hypovolemic or diuretics if they're fluid overloaded to help clear 14:13 the fluid. 14:15 Stop nephrotoxins we talked about earlier, treat the underlying cause, again if 14:19 it's 14:20 an infection, use antibiotics if it's renal stone, treat the pain but also try 14:24 to remove 14:24 the stone if it's big, if it's an obstructed catheter try flushing it. 14:31 Take underlying complications of acute kidney injury, mainly electrolyte imbal 14:36 ances. 14:36 Some of these complications can get out of hand and so some patients will 14:40 require dialysis. 14:43 So indications for acute dialysis in a scenario where someone has acute kidney 14:48 injury, you 14:49 can easily remember with the acronym AEIOU. 14:56 So A is for acidosis which is refractory, it doesn't change. 15:00 E is for electrolyte imbalance, specifically refractory severe hyperklemia. 15:06 Intoxication or ingestion you can remember as the acronym SLIME. 15:11 So these toxins include salicylic acid, too much lithium, isopropanol, 15:19 magnesium laxatives, 15:21 ethylene glycol. 15:26 O is for overload, so fluid overload that just is persistent. 15:32 And U is for uremic complications because with acute kidney injury, as well as 15:37 chronic 15:37 kidney injury, urea can be so high and can lead to complications such as peric 15:42 arditis, 15:43 as well as platelet dysfunction leading to bleeding. 15:45 And these are some indications for acute dialysis to remove all this waste from 15:49 the blood. 15:50 Thank you for watching, I hope you enjoyed this video. 15:56 Thank you. 15:57 Thank you.