Hyperemesis Gravidarum
At least 80% of women experience nausea and vomiting. Hyperemesis gravidarum is a condition of pregnancy characterized by intractable nausea, vomiting and dehydration and is estimated to affect ~2% of pregnancy women.
Definition
Morning sickness: early pregnancy nausea/vomiting usually disappearing after the first trimester
Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Unlike morning sickness, hyperemesis gravidarum is a complication of pregnancy characterised by persistent uncontrollable nausea and vomiting that persist beyond the 20th week of pregnancy.
Clinical Manifestation
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Irritability
- Distress (both the mother and for the featus)
- Weight loss
- Dehydration (may cause ketosis and constipation)
- Malnutrition
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Remember
That hyperemesis gravidarum tends to begin somewhat earlier in the pregnancy and last significantly longer than morning sickness. 10-20% of cases may last the entire pregnancy.
Investigations
- LFT – ↑AST and ALT
- FBC – signs of dehydration
- Urinalysis – Presence of ketones
- EUC – electrolyte imbalance and signs of dehydration (urea)
- Hypokalaemia
- Hyponaturamia
- Hypochloraemic alkolosis
- Vaginal/pelvic ultrasound – if suspect molar or multi pregnancy
Diagnosis is considered by exclusion of the other things
Think
In the second half of pregnancy, nausea and vomiting may be symptom of labour, preeclampsia, gallstones, appendicitis or acute fatty liver of pregnancy.
Treatment
- Reassure
- Education
- IV fluids
- Correct electrolytes
- Antiemetic (promethazine, odansetron)
Complications
- Weight loss
- Dehydration
- Metabolic acidosis from starvation
- Alkalosis from loss of HCl
- Hypokalaemia (electrolyte imbalance)
- Mallory-Weiss tears
- Peripheral neuropathy from Vitamin B12 and B6 deficiency
- Wernicke’s encelopathy (worse case)
Gestational diabetes mellitus
Overview
Defined as any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy.
- Heterogenous group / may include unrecognised pre-exiting DM
- Implications for both baby and mother
- Metabolic changes in pregnancy lower glucose tolerance
- Insulin demands increase during pregnancy
- Normal physiological process in majority of women
More info on Gestational Diabetes
Definition
Diabetes Mellitus: metabolic condition characterised by chronic hyperglycaemia as a result of defective insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
Gestational Diabetes: Defined as any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy.
Pre-gestational Diabetes: Diabetes diagnosed BEFORE pregnancy.
Risk factors
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- >35 years of age
- Obesity
- Family history
- Past history of GDM
- previous adverse pregnancy outcome
- Ethnic group at higher risk for GDM
Diagnosis
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Remember
Screen for GDM in high risk patients at 24 and 28 weeks gestation.
Treatment
- Team approach
- Obstetrician
- Endocrinologist
- Diabetes educator/dietician
- Midwife
- Paediatrician
- Education women (and partners)
- Implications of GDM for baby and mother
- Dietary and exercise recommendations
- Self monitoring of BSL
- Insulin if BSLs remain high
- Fetal surveillance
- No set regime
- Usually weekly cardiotocography commenced at 36 weeks in GDM requiring insulin
Timing of delivery (Parturition)
- Controlled GDM (diet): as per normal
- Well-controlled GDM (insulin): 28-39 weeks
- Earlier delivery if poor BSL control/polyhydramnios/ other obstetric complication
Why treat GDM?
- Reduction in composite outcome of death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture and nerve palsy
- Reduction in infants weighing >90th birth-centile.
Venous-Thrombo Emoblism
Overview
Pregnancy is a hypercoagulable state that returns to normal 4 week after delivery. The hypercoagulability is particularly relevant at delivery, with placental seperation. Pregnancy is a risk factor for venous thromboembolism because of:
- Virchow’s triad: venous stasis/procoagulant factors increased anticoagulants factors reduced/ vessel wall injury during labour and CS
- Proinflammatory state with activation of endothelial cells
- Maternal factors further increase risk during pregnancy
- Important cause of maternal morbidity and mortality
Epidemiology
- 4-5 fold increased risk compared to non-pregnant women of the same age
- ~1/2 of VTE occur postpartum
Risk Factors for VTE postpartum
- Previous VTE
- Age >35
- Obesity
- Active medical illness
- Smoking
- Family history
- Varicose veins
- Immobility
- Multiple pregnancy
- Pre-eclampsia
- Assisted reproduction technology
Thromboembolism in Pregnancy
- Superficial thrombophlebitis
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Thrombophilias
Clinical Manifestation
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- 50% asymptomatic
- Leg pain and swelling – Left lower leg (most common)
- Palpable cord over ther course of the invovled superficial veins
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Pleuritic chest pain
- Dyspnoea, tachypnoea
- Air hunger
- Palpitations, tachycardia
- Haemotptysis
Diagnosis of acute DVT/PE
- Any women with signs and symptoms should have ohjective testing and treatment with low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)
- DVT: Duplex Ultrasound +/- Magnetic Resonance venography +/- V/Q scan +/- CT pulmonary angiogram
- PE: Chest X-Ray +/- Duplex Ultrasound +/- V/Q scan +/- CT pulmonary angiogram
Prevention (Prophylaxis)
Mechanical methods
- Mobilisation
- Compression stockings
- Calf stimulation
- Pneumatic compression
Pharmacological
- Heparin: does not cross placenta
- Warfarin: NOT antenatally, postpartum ok
- Both heparin and warfarin safe for breastfeeding
Anaemia
Overview
Anaemia is the commonest medical disorder in pregnancy. It is responsible for significant high maternal and fetal mortality, more so in developing nations.
Pathophysiology
- Erythropoesis is the synthesis of red blood cells. For proper erythropoesis adequate nutrients are needed:
- Minerals – Iron
- Vitamins – Folic acid, Vitamins b12, Vitamin C
- Proteins – for synthesis of globin moiety
- Hormones – Androgens and thyroxine
- In pregnancy there is increase in total blood volume as well as the red blood cell mass. However, the increase in plasma volume (50%) is more then the increased red blood cell mass and total haemoglobin (25%). Thus the blood is “diluted” resulting in physiological anaemia.
Definition
Anaemia:
Anaemia in Pregnancy: Haemoglobin <10.5g/dL
Post Partum anaemia:
Aetiology
- Iron Deficiency (most common)
- Folate deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
Clinical Manifestation (also depends on the type of anaemia)
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Palpitations
- Breathlessness
- Dizziness
- Syncope
- Pallor
- Glossitis
- Stomatitis
- Oedema
- Hypoproteinaemia
Investigations
- FBC
- Blood smears
- Iron studies
- Serum folate
- Serum Vitamin B12
Treatment
- Iron Deficiency – Oral iron supplements + Vitamin C (orange juice) as this increases iron absorption. Parental iron if oral iron can not be tolerated.
- Folate deficiency – folic acid given preconception and in early pregnancy to reduce ris of neural tube defects. Daily if high risk of neural tube defect.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency – Vitamin B12 supplement
| High Risk of Fetal Neural Tube Defect |
| On anticonvulsants |
| Previous child with neural tube defect |
| Folate deficiency |
| Diabetes |
| BMI >35 |
| Sickle cell disease |
Complications
- Maternal effects of anaemia
- Antenatal – poor weight gain, preterm labour, pre-eclampsia, abruptio placentae
- Intranatal – dysfunctional labour, Postpartum haemorrhage
- Postnatal – Sepsis
- Fetal effects of anaemia
- pre-maturity
- Intrauterine Growth restriction
- Low birth weight
- Anaemia in infancy
- Failure to thrive
- Poor intellectual development
- Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in adult lives.
Hypertension
Normal Pregnancy
- Characterised by a fall in BP
- Usually nadir in 2nd trimester
- BP rises towards preconception and levels towards end of 3rd trimester
Hypertension in Pregnancy
- Systolic BP >140mmHg and/or Diastolic BP >90 mmHg
- Both systolic and diastolic blood pressure is important
- Severe Hypertension
- Systolic BP >170mmHg and/or Diastolic BP >110 mmHg
Classification
- Chronic hypertension – coming into pregnancy
- Gestational hypertension – During pregnancy
- Preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension
- Pre-eclampsia (discussed next section) – it affects 5% of pregnancies
Chronic hypertension
- Essential hypertension (>140/90) before pregnancy or <20weeks without known cause
- Secondary causes include:
- Chronic kidney Disease
- Renal artery stenosis
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Pheochromocytoma
- Cushing’s disease
- Coarctation of aorta
Gestational Hypertension
- New onset hypertension >20 weeks without maternal or fetal features of preeclampsia
- Some women (25%) will develop preeclampsia
- If BP increase >12 weeks post partum: classify as chronic hypertension
- Near term, little increase in adverse pregnancy outcomes
- Early and sever hypertension more likely to develop preeclampsia and adverse pregnancy outcome
Preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension
- Preexisting Hypertension strong risk factor for preeclampsia
- Superimposed pre-eclampsia >20 weeks in women with chronic hypertension
In women with pre-existing proteinuria, diagnosis is difficult.
Pre-Eclampsia
- Unique human disorder
- Affect only pregnant women – occurs in ~5% of pregnancys and mainly occurs in primigravid women.
- A placental disease
- Clinical manifestation involve multiple organ systems
- Delivery remain the only cure
| Watch Video Pre Eclampsia – Overview |
Clinical Presentation
- Headaches
- Visual scintillations
- Epigastric or right upper quadrant pain radiating into the back (hepatic ischaemia)
- Oligouria
- Lower abdominal pain (placental abruption)
- Reduced fetal movements
Clinical Examination
- Hepatic tenderness or enlargement
- Hyper-reflexia or clonus
- Pulmonary oedema
- Signs of fetal growth restriction
- Oedema
Think
Oedema is not used for diagnosing Pre-eclampsia as this can be normal in pregnancy.
Diagnosis Hypertension >20 weeks + one of more of
Renal involvement
- Proteinuria
- Increased plasma creatinine
- Oliguria
Neurological involvement
- Convulsion (eclampsia)
- Hyperreflexia with clonus
- Severe headache
- Persistent visual disturbances
- Stroke
Risk Factors
- Primigravidum
- Previous pre-eclampsia
- Family histroy
- Multiple pregnancies
- Diabetes
- Pre existing hypertension
- Renal disease
- Connective tissue disorders (eg. Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE)
- Obesity
Side note
Smoking is said to be a protective factor. Smoking is also protective against Ulcerative colitis and Parkinson’s Disease.
Pathophysiology
- In normal pregnancy there is a fall in Bp
- In Preeclampsia theses normal physiological changes fail
- Vasconstirction
- Platelet activation with intravascular coagulation (usually local but occasionally disseminated)
- Maternal plasma volume contraction
- Endothelial dysfunction in a variety of vascular beds
Investigation
Help distinguish pre-eclapmsia from chronic hypertension and gestational hypertension and to assess extent of condition.
- Preeclampsia bloods
- FBC
- EUCs
- LFT
- Urate
- Fetal assessment
- Cardiotocography
- Ultrasound: fetal growth/restriction, amniotic fluid and umbilical artery flow.
Treatment
- Assess need for delivery
- Control severe hypertension – Methyldopa, oxprenonlol, labetolol or clonidine
- Usually start antihypertensive if BP 140-160/90-100
- Antenatal corticosteroids for lung maturation (<34weeks)
- Post-partum management – Manditory to assess preeclamptic women for several months to check if blood pressure returns to normal.
| Indications for Delivery |
| Progressive Maternal organ dysfunction |
| Inability to control Blood pressure |
| Fetal well-being concerns. |
Remember
ACE inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor blockers are teratogenics and should be avoided. Diuretics are generally avoided in Pre-eclampsia.
Complication
- Eclampsia means convulsions. It is very uncommon but is very dangerous.
If Eclampsia
- Resuscitate
- Seizure usually self-limiting
- IV Diazepam or clonazepam if seizure prolonged
- Magnesium sulphates
- Prevent further seizures
- Control hypertension
- Delivery
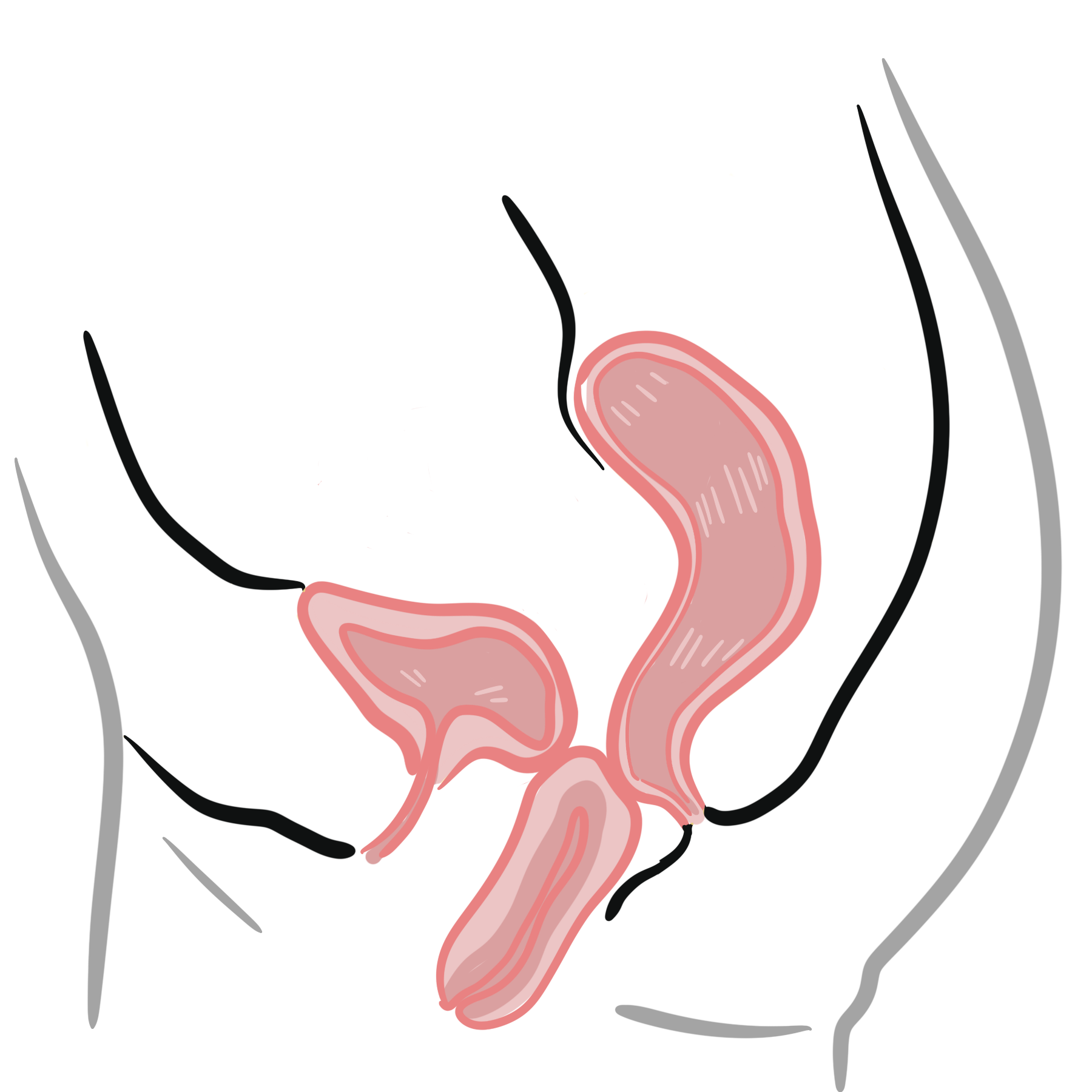
PV bleeding in Pregnancy
| CAUSES OF VAGINAL BLEEDING IN PREGNANCY | ||
| 1st Trimester | 2nd Trimester | 3rd Trimester |
| Miscarriage | Miscarriage | Pregnancy “Show” |
| Trophoblastic disease | Trophoblastic disease | Vasa praevia |
| Ectopic Pregnancy | Abruptio placentae | Abruptio placentae |
| Placenta praevia | Placenta praevia | |
Remember
Other non-pregnancy related include infection, vaginal ulcers, vaginal inflammation, cervical erosions, cervical polyps, coagulation disorders, trauma.
Side note
Miscarriage is common, occurring in at least 15-20% of pregnancies.
For more information on PV bleeding in Pregnancy.
Antepartum Haemorrhage
Overview
Antepartum haemorrhage is per vaginal bleeding during/associated with pregnancy after 20 weeks gestation. Antepartum haemorrhage is usually associated with the placenta.
Definition
Antepartum Haemorrhage: Any bleeding from the genital tract after the 20 th week of pregnancy and before the onset of labour.
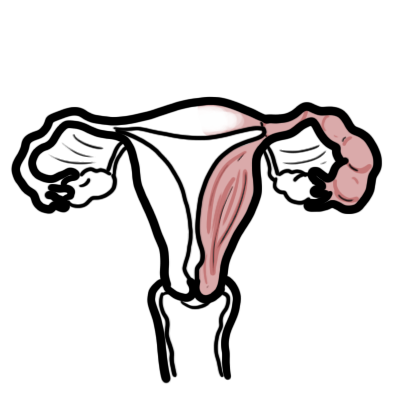
Placenta Praevia: Low-lying placenta – inserts wholly or partially into the lower uterine segment and can cover the internal os.
Placental Abruption: The premature separation of a normally sited placenta from the uterus.
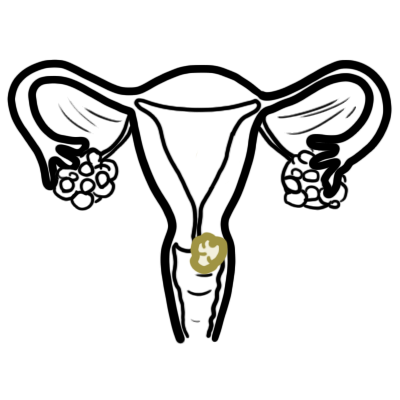
Vasa Praevia: Rare condition in which the umbilical vessels, unsupported by either the umbilical cord or placental tissue, traverse the fetal membranes of the lower segment above the cervix.
Postpartum Haemorrhage: a blood loss exceeding 500ml after delivery of the infant. It is divided into Primary (<24hours of delivery) or Secondary (>24hours – 6weeks).
Aetiology
- Placenta praevia (20%) – 4 grades
- Placental abruptio
- Vasa praevia
- Unknown cause (50%)
- Other (~1%)
- Maternal factors: cevical erosion, cervicitis, vaginitis, a show, gential tract tumours, traumas
- fetal factors: vasa praevia
Remember
Never perform a vaginal examination in presence of PV bleeding without first excluding a placenta praevia.
Side note
Women with an placental abruption will usually present in pain with a tense uterus. 70% of placental abruption occurs in low-risk pregnancies.
Severity
- Spotting – staining, streaking or blood spotting noted on underwear or sanitary products
- Minor haemorrhage – blood loss & <50mL that has settled
- Major haemorrhage – blood loss of 50-500mL with no signs of clinical shock
- Massive haemorrhage – blood loss of 500-1000mL and/or signs of clinical shock
| Risk Factors |
| Abnormal placental insertion |
| Vasa praevia |
| Abnormal cord insertion into the placenta |
| Trauma |
| Substance use |
| Hypertension |
| Past history of APH |
| Multiple pregnancy |
| High parity |
| Polyhydramnios |
| Uterine anomalies or tumours |
Side note
60% of women who experience an antepartum haemorrhage have no identified risk factors.
Clinical Presentation
- Per Vaginal Bleeding
- Abdominal pain
Clinical Examination
- Distress
- Palpate Uterus
- Placenta praevia: soft uterus, normal uterine tone, high presenting part
- Placental abruption: pain, tender, firm/tense uterus
Remember
Never do a digital vaginal examination until ultrasound has confirmed it is not placenta Pravia.
Investigations
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- FBC
- EUC
- LFT
- Blood group & hold + cross match
- Coagulation studies
- Kleihauer-Betke test or flow cytometry
- CTG – signs of fetal distress
Treatment Either active or expectant management
- Assess vitals
- Oxygen
- Insert two large bore cannulas
- Bloods for invesitgation (above)
- Fluid replacement
- Cross match
- Resuscitation and/or deliver
- Fetal welfare assessment (CTG)
- Steroid cover if preterm baby
- Anti D if Rh -ve
- Maternal education and support
- Preperation for transfer/paediatrician present for delivery
Maternal Complications of Antepartum Haemorrhage
- Anaemia (monitor serum Hb and iron studies)
- Haemorrhagic shock
- Postpartum haemorrhage (should be anticipated)
- Renal tubular necrosis and acute renal failure
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy (DIC)
- Uterine rupture
- Infection
- Death
- Invasive placental implantation (accrete/increta/percreta)
- Psychological sequelae
- Complications of blood transfusion
Foetal Complications of Antepartum Haemorrhage
- Fetal hypoxia & CNS damage
- Small for gestational age and fetal growth restriction
- Prematurity (iatrogenic and spontaneous)
- Fetal death









Discussion