Obesity

Expenditure – Base Metabolic Rate (70%), thermogenesis (20%), exercise (10%). Base metabolic rate Approximately 1800 calories a day for 70kg man.Increase BMR – Sever exercise, fever, catecholamines, caffeine, thyroid hormones, smokingDecrease BMR – Age, female 10% below male, menopause.
Assess any environmental, social, and family factors, including family history of overweight or obesity and comorbidities.
Clinical Presentation
Physical examination
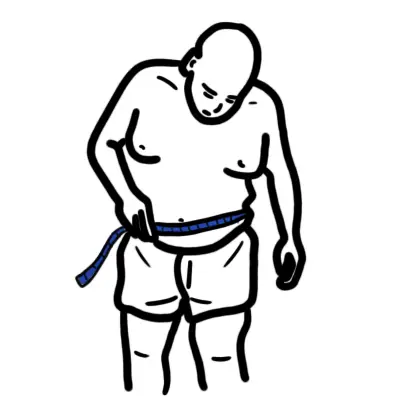
Assessment of weight and obesity
| Limitations of BMI on: |
| Muscular people |
| Elderly people |
| Young children (centile charts) |
| Classification | BMI | Risk of morbidities |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | <18.5 | Increased |
| Normal weight | 18.5–24.9 | Low |
| Overweight | >25 | Increased |
| Obese I | 30–34.5 | Moderate |
| Obese II | 35.0–39.9 | Severe |
| Obese III | >40 | Very severe |
An adult’s waist circumference is measured halfway between the inferior margin of the last rib and the crest of the ilium in the mid-axillary plane. The measurement is taken at the end of normal expiration.
Investigate comorbidities and other factors to an appropriate level, depending on the person, timing of assessment, degree of overweight or obesity, and previous assessments.
| Facts about obesity |
| Genetics factors play a big role, but heritability is not destiny. Life-style modification (environmental change) can promote weight loss as much as pharmaceutical agents available |
| Trying to go on a diet is effective in losing weight but generally does not work well in the long-term |
| Exercise increases health regardless of body weight or weight lost |
| Physical activity or exercise in a sufficient dose aids in long-term weight maintenance |
| Continuing doing things that promote weight loss helps maintain weight loss |
| Programs that involve overweight children and their parents help promote greater weight loss or maintenance |
| Meal replacement products help promote greater weight loss |
| Pharmaceutical medication can help with weight loss and maintenance as long as the agents continue to be used. |
| In appropriate patients, bariatric surgery results in long-term weight loss and reductions in the rate of incident diabetes and mortality |
Significant benefit (a reduction in mortality and morbidity) can be obtained with moderate weight loss (5-10%). Energy Balance is key!
Lifestyle modifications
Medications can have an adverse effect on weight by influencing either food intake (hunger) or energy expenditure. Medication should be considered in people who have a BMI >25
Bariatric Surgery
The most effective treatment for the morbidly obese
| Indications for Bariatric Surgery |
| Other approaches were unsuccessful |
| BMI >35 |
| Understands surgery and risks |
| No uncontrolled psychological conditions |
| Dedicated to life-style change and follow-up |
Metabolic Syndrome is a cluster of risk factors comprising of excess abdominal weight, lipid abnormalities, hypertension and elevated glucose levels.

Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Discussion