For more information: Parturition and Routine Care
| NORMAL EXPECTED PHYSIOLOGICAL VALUES AT DIFFERENT AGES | |||
| Age (years) | Respiratory Rate | Heart rate | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| <1 | 30-40 | 110-160 | 70-90 |
| 1-2 | 25-35 | 100-150 | 80-95 |
| 2-5 | 25-30 | 95-140 | 80-100 |
| 5-12 | 20-25 | 80-120 | 90-110 |
| >12 | 15-20 | 60-100 | 100-120 |
Oxygen saturation return to 100% after 10 minutes post partum.
| RISK FACTORS FOR PREMATURE BABY | |
| Maternal | Fetal |
|
|
| Placental | Social |
|
|
| Remember All pregnant women between 24 and 34 weeks at risk of preterm birth should be offered treatment with a single course of antenatal corticosteroids to promote lung development (induction of type II pneumocytes) |
Follow the neonatal resuscitation guideline in needed.
| Short Term Complication of Prematurity | |
| Respiratory | Respiratory Distress syndrome Apnea |
| Cardiac | Patetent ductus arteriosus |
| Neurological | Intraventricular haemorrhage Periventricular leukomalacia |
| Hepatic | Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Hyperbilirubinaemia |
| Renal | Immature kidney |
| Gastrointestinal | Feeding problems Necrotizing enterocolitis |
| Haemotological | Anaemia |
| Immunologial | Infection |
| Long term complication of prematurity |
| Delayed Growth |
| Retinopathy |
| Chronic lung disease |
| Neurodevelopment delay |
| Remember Jaundice <24hours is abnormal (pathological) and >24 is often normal |
Jandice is common in the newborn (50%) and is almost always caused by unconjugated bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia can lead to kernicterus (brain damage)
Management for Jaundice after 24hours
| Watch Bilirubin Metabolism |
Respiratory distress is common immediately after birth, and is typically caused by abnormal respiratory function during the transition from fetal to neonatal life
Sign and symptoms
Persistent Pulmonary hypertension: With the first breath pulmonary vascular resistance falls and there is a rush of blood to the lungs. This process is partly mediated by nitric oxide and initiates the change from fetal to adult circulation. This process may be interrupted in various conditions (RDS, TTN, meconium aspiration, etc), and as a result pulmonary hypertension develops.
Abnormal persistence of elevated pulmonary vascular resistance that leads to right-to-left shunting of deoxygenated blood through the foramen ovale and the ductus arteriosus, resulting in hypoxemia.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome or "hylane membrane disease" is caused by deficiency of surfactant, the phospholipid mixture that reduces alveolar surface tension, which decreases the pressure needed to keep the alveoli inflated, and maintains alveolar stability. When surfactant is deficient it can lead to atelectasis, re-inflation with each breath exhausts the baby, and respiratory failure follows. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia can further complicate things premature infants with RDS. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia persistent hypoxia +/- difficult ventilator weaning.
More info on RDS
Transient Tachypnoea of Neonate or "wet lung syndrome" is caused by failure of adequate lung fluid clearance at birth, resulting in excess lung liquid. The liquid fills the air spaces and moves into the extra-alveolar interstitium, where it pools in perivascular tissues and interlobar fissures until it is cleared by the lymphatic or vascular circulation.
| Remember Common in term infant delivered by Cesarean section or rapid second stage labor. Rapid improvement generally within hours to a few days. |
Pneumonia (GBS or e-coli)
Meconium aspiration syndrome occurs in the term/near term infant when meconium, the faecal material that accumulates in the fetal colon during gestation, is passed in utero, leading to meconium obtained amniotic fluid. It may lead to airway obstruction, surfactant dysfunction, pulmonary vasoconstriction, infection and chemical pneumonitis.
| Remember Chest X- ray may reveal patchy infiltrates, increase AP diametes, flattening of diagphragm |
Pneumothorax
Apnoea is a common problem until about 24 weeks gestation. Management with CPAP and close monitoring.
Sepsis should always be a differential diagnosis in an unwell child.
Aetiology and Management:
More info on Paediatric Sepsis
| Remember Most common organisms in the neonate are group B streptococcus, E. coli and listeria monocytogenes |
| Watch: Neonatal Infections Overview |
| Normal | Abnormal |
| Naevus flammeus | |
| Milia | |
| Miliaria | |
| Erythema toxicum | |
| Mongolian blue spot |
Vomiting is normal. However, bilious (green) vomiting in neonates always needs urgent help or prompt investigation and management
Necrotising enterocolitis is an inflammatory bowel necrosis. Prematurity is a major risk factor. Perforated NEC associated with 40% mortality in neonates
Gastroenteritis
Bowel Obstruction: Malrotation, volvulus, intussusception, duodenal atresia (associated with Down's syndrome), Meconium ileus (associated with cystic fibrosis)
Pyloric stenosis: Hypertrophy of the pyloric smooth muscle in early infancy, which occurs at about 3-6 weeks causing classical projectile vomiting after meals.
Hurschrung's disease: Congenital absence of ganglia in a segment of colon leading to functional GI obstruction, constipation and megacolon.
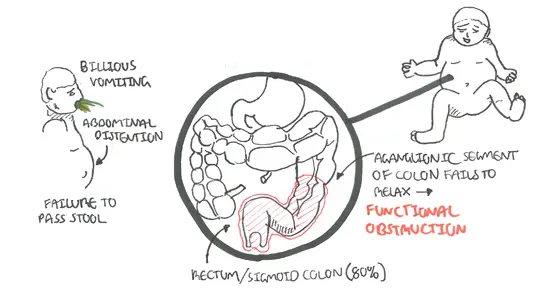
Hurschrung's disease typically effects the distal colon, sigmoid/rectum and causes dysmotility leading to a non-mechanical obstruction.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a developmental defect in the diaphragm allowing herniation of abdominal contents into the chest. This leads to impaired lung development (pulmonary hyperplasia and hypertension).
Oesophageal atresia and Tracheo-oseophageal fistula is a spectrum of abnormalities with Oseophageal atresia plus a distal Tacheo-oesophageal fistula being the most common (86%).
Inguinal Hernias are due to patent processus vaginalis (the passage which ushers the descending testicle into the scrotum). Require prompt surgical referral as the frequently strangulate.
Abdominal wall (umbilical) defects
Undescended testis (cryptochidism) testicular descent from the fetal abdominal site into the scrotum is normally complete by birth. Absence of a scrotal testis may be due to agenesis, intrabdominal arrest, incomplete descent, or ectopic descent. Incidence of 2-4% in newborn. Commoner on the right sire.
Posterior urethral valve presents with oligohydramnios or absent or feeble voiding (+/- uraemia and a palpable bladder).
Congenital/genetic disorders
Foreskin
Scrotal swelling
Congenital Heart Disease
Cynotic (right to left shunt - remember the 5T's)
Acynotic (Left to right shunt - remember the 3Ds)
Cardiovascular Infection
Seizures Febrile Seizure and Epilepsy classify seizures differently.
Classification
Management (Anticonvulsants)
More info on Paediatric Seizures
Neural Tube Defect
Neural tube defects (NTDs) result from failure of the neural tube to close between the 3rd and 4th week of in utero development.
NTDs are the second most common congenital anomaly after congenital heart defects.
NTDs of the spinal cord (most common)
NTDs of the brain
NTDs of both the brain and spinal cord
Cerebral Palsy
More information on cerebral palsy
Hydrocephalus is an abnormal excess of CSF in the ventricular system of the brain.
More info on Hydrocephalus
Common Birth Defects
More info on Birth Defects
Most Transplacental Intrauterine Infections are acquired in first of second trimester.
TORCH
More info on Infectious Disease in Pregnancy
